Understanding UTXO and the Double-Spending Problem in Blockchain
2 Key Concepts UTXO and Double Spending in Blockchain – Blockchain technology, with its decentralized nature, has transformed the way we think about transactions and money. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin rely heavily on the concept of Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXO) and the double-spending problem to ensure the integrity and security of transactions. But what exactly do these terms mean, and why are they so important in the world of blockchain?
What is UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output)?
To understand UTXO, let’s first talk about how cryptocurrency transactions work. When you send cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, you’re essentially creating a transaction where you’re transferring ownership of a certain amount of coins. But how does the blockchain know you have the coins you’re sending? This is where UTXO comes in.
In the Bitcoin network, all transactions are based on inputs and outputs. Here’s how it works:
- Inputs refer to the source of funds you’re spending (essentially the cryptocurrency you previously received).
- Outputs are the destinations where you’re sending your cryptocurrency (the recipient’s address).
Each output, once it has been sent and used, is considered spent. However, if you haven’t yet used an output in a transaction, it is an unspent transaction output—or UTXO.
UTXO Example in Real Life
Let’s imagine that Sarah has 2 Bitcoins, and she wants to send 1 Bitcoin to her friend Bob. She might have received those 2 Bitcoins from two previous transactions, each worth 1 Bitcoin.
- Sarah has 2 separate UTXOs: one with 1 Bitcoin and another with 1 Bitcoin.
- To send 1 Bitcoin to Bob, she uses one of those UTXOs as the input in her transaction.
- The transaction sends 1 Bitcoin to Bob’s address, and the remaining 1 Bitcoin becomes a new UTXO that Sarah can use in the future.
In this scenario, Sarah has used a UTXO to pay Bob, and the blockchain now knows that Sarah no longer has that 1 Bitcoin.
What is the Double-Spending Problem?
The double-spending problem is a fundamental issue in digital currencies. In traditional money systems, physical cash can’t be spent twice. If you hand someone a $10 bill, you no longer have that $10—it’s gone. However, in the digital world, it’s easy to duplicate data, and there’s a risk that someone could try to spend the same digital currency more than once.
This is known as double spending. Imagine Sarah trying to send the same Bitcoin to Bob and Alice at the same time—this would mean Sarah is trying to double spend her Bitcoin, which would lead to fraud and invalid transactions.
Real-Life Example of Double-Spending
Let’s say Sarah tries to send 1 Bitcoin to Bob using one UTXO, but at the same time, she tries to send the same Bitcoin to Alice using the same UTXO. This is a double-spend attack, and if the blockchain doesn’t prevent this, it could create chaos.
In traditional systems, double spending is prevented by a central authority, like a bank. However, Bitcoin’s decentralized nature means there’s no central authority to prevent double spending. Instead, the Bitcoin network uses a consensus mechanism to resolve this issue.
How Does Blockchain Prevent Double Spending?
Blockchain, with its decentralized ledger, ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or replicated. Here’s how blockchain prevents double-spending:
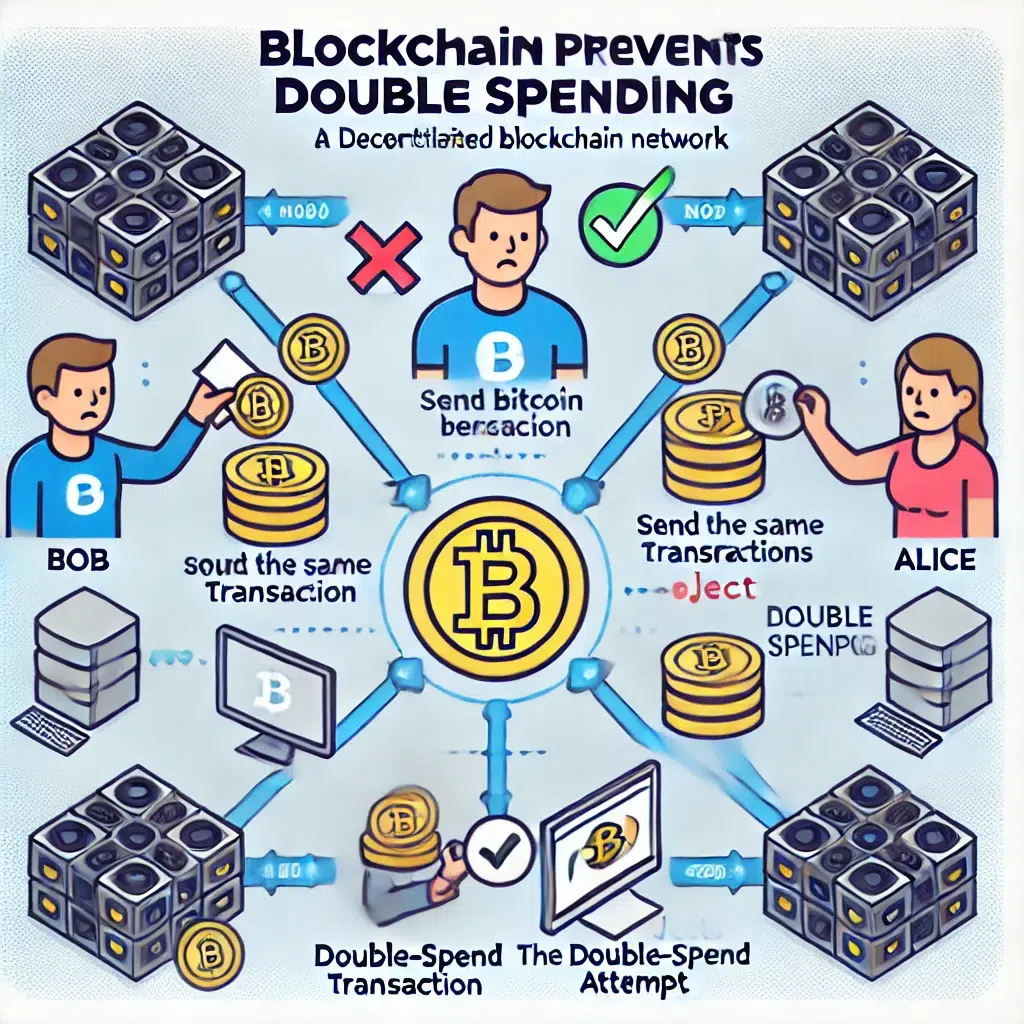
- Transaction Verification: Every transaction on the blockchain is verified by the network. When Sarah tries to send 1 Bitcoin to both Bob and Alice, the network checks if the UTXO she’s using is valid. If the Bitcoin has already been spent, the network will reject the transaction.
- Proof of Work (PoW): Miners use Proof of Work (PoW) to validate transactions. PoW requires miners to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to add a block to the blockchain. If someone tries to double spend, the blockchain will reject it because only one valid transaction will be accepted by the network.
- Consensus Mechanism: The Bitcoin network relies on consensus between participants. In case of conflicting transactions, the longest chain of blocks (i.e., the chain with the most accumulated work) is considered the valid one. This ensures that the first valid transaction takes precedence, and any subsequent attempts to double spend are rejected.
The Importance of UTXO in Blockchain Security
UTXO plays a key role in ensuring the integrity and security of the blockchain. It serves as the mechanism that guarantees that the cryptocurrency being spent hasn’t already been used. Here’s why UTXOs are so crucial:
- Transparency and Security: UTXOs are publicly recorded on the blockchain, making it easy for anyone to verify whether a particular coin is available to be spent or not.
- Preventing Double Spending: Since each UTXO is tied to a unique transaction and address, it’s impossible to double-spend the same coin without being caught by the network.
- Efficient Transaction Tracking: By using UTXOs, the blockchain can efficiently track which coins belong to whom and which coins have already been spent.
Advantages of UTXO and Blockchain in Preventing Double-Spending
Now that we understand how UTXO works and how double-spending is prevented, let’s look at the advantages of this system.
1. Security
The decentralized nature of blockchain, combined with UTXOs, makes the system highly secure. Since there’s no central authority, it’s difficult for hackers to manipulate the system. The consensus mechanism ensures that double-spending attempts are detected and rejected.
2. Transparency
All UTXOs are publicly recorded on the blockchain, making it easy for anyone to verify transactions. This transparency ensures that the system is open and trustworthy, and it prevents fraud.
3. Efficiency
UTXOs make transactions more efficient. Instead of keeping track of account balances, the blockchain tracks unspent outputs. This ensures that each transaction is validated in real-time and that the network can handle large volumes of transactions without slowing down.
4. No Double-Spending
The key advantage of UTXOs is that they prevent double-spending. Each UTXO can only be spent once, and since all transactions are verified by miners, there’s little risk of fraud or duplication.
Disadvantages of UTXO and Blockchain
Despite its advantages, the UTXO model and blockchain technology come with some limitations:
1. Scalability
The UTXO model requires each transaction to reference previous outputs, and this can create scalability issues. As more transactions are made, the blockchain grows in size, which could eventually lead to slower transaction speeds and higher fees.
2. Complexity for Users
For average users, dealing with UTXOs can be confusing. Every time a user spends cryptocurrency, they need to select which UTXOs to use. If someone has many small UTXOs, it can be challenging to manage and optimize transactions.
3. Transaction Fees
Since UTXOs must be included in transactions, the number of UTXOs a user has can affect transaction fees. Larger transactions that involve more UTXOs may require higher fees, which can be a disadvantage for users with many small outputs.
4. Security Risks for Miners
While blockchain technology is secure, miners are still vulnerable to attacks, including 51% attacks, where an attacker gains control of the majority of mining power. This could allow them to rewrite parts of the blockchain, leading to double-spending or other malicious activity.
2 Key Concepts UTXO and Double Spending in Blockchain – FAQs
What’s the difference between UTXO and account-based models?
In a UTXO model, transactions are based on inputs and outputs, where each coin is represented by a unique transaction output. In an account-based model, like Ethereum, users’ balances are tracked in a centralized ledger, making it easier to manage but potentially more vulnerable to attacks.
Can UTXOs be merged?
Yes, UTXOs can be merged. When a user wants to send more cryptocurrency than a single UTXO holds, they can combine multiple UTXOs into one transaction to cover the total amount.
Is double spending possible in Bitcoin?
Double spending is theoretically possible, but Bitcoin’s blockchain uses consensus mechanisms and proof of work to ensure that only one valid transaction gets recorded. Attempts to double spend are rejected by the network.
Summary
UTXO and the double-spending problem are fundamental to understanding how cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin maintain their security and integrity. UTXOs ensure that each coin can only be spent once, while the blockchain’s consensus mechanisms prevent double-spending by verifying transactions across a decentralized network. This system is highly secure, transparent, and efficient, but it does have challenges, particularly around scalability and transaction fees.
Cardano Staking and Midnight Blockchain in 2025
What Are Avalanches 3 Blockchains?
Hey everyone! If you have any questions or thoughts, feel free to drop a comment. Let’s learn and discuss together. Your feedback is always welcome!