Introduction Big Data – Big Data has emerged as a crucial field in today’s technology-driven world, where vast amounts of information are generated every second. This article explores the concept of Big Data through a simple story, real-life examples, and its impact on various industries.
Understanding Big Data – A Journey from Libraries to Digital Landscapes
Imagine a time when libraries were the primary source for accessing knowledge. People would visit libraries to search for books, which was manageable due to the small population and limited variety of literature. However, as the population grew, so did the number of books and written works, making it increasingly challenging to find the desired materials. This situation required a technological solution, leading to the advent of digital libraries and online resources. This transition mirrors the evolution of data in our modern world. Initially, organizations managed small amounts of data with traditional methods. But as data generation accelerated, it became apparent that these methods were insufficient. The concept of Big Data emerged to address the challenges posed by this rapid growth.
What is Big Data? | Introduction Big Data
Big Data refers to large volumes of data that are generated every day and grow exponentially over time. The traditional methods of storing and processing data have become inefficient in handling such vast amounts. Big Data encompasses not only the volume of information but also the speed (velocity) at which it is generated and the variety of formats in which it exists.
Real-Life Examples of Big Data Generation | Introduction Big Data
- Social Media: Platforms like Facebook generate an astonishing four petabytes of data daily. This includes everything from photos and posts to comments and likes. For instance, approximately 65,000 photos are shared on Instagram every minute, illustrating the massive scale of data produced.
- Emails: Emails have become essential for communication, with about 300 billion emails sent every day. Each email can contain various attachments, such as documents, images, and videos, contributing to the vast amount of data that must be managed.
- Banking Transactions: The banking sector processes over 100,000 transactions per second, each requiring accurate record-keeping. A single error in these records can lead to significant issues, highlighting the importance of efficient data management.
- E-Commerce: Online shopping platforms like Amazon and Flipkart generate massive amounts of data related to user behaviors and preferences. For example, if a user searches for a product, targeted advertisements will appear based on their activity, all made possible through Big Data analytics.
The Necessity of Big Data | Introduction Big Data
With the explosion of data, traditional storage and management methods have proven inadequate. Big Data provides solutions for:
- Handling Unstructured Data: Transforming unstructured data into structured formats is essential for analysis and decision-making.
- Improving Customer Service: Big Data enables personalized experiences, allowing businesses to tailor services and recommendations to individual customers.
- Creating Marketing Campaigns: Organizations can develop targeted marketing strategies based on user data, enhancing customer engagement and driving sales.
- Insurance and Risk Assessment: In the insurance sector, Big Data analytics helps in assessing risks more accurately, ultimately benefiting both companies and customers.
According to the IDC report, the amount of data created per person is expected to reach 1.7 MB per second by 2020, with total global data anticipated to hit 44 Zettabytes (44 trillion Gigabytes) and 175 Zettabytes by 2025. The volume of data is doubling approximately every two years, highlighting the exponential growth in data production due to smart electronic devices and other sources. For detailed statistics, you can refer to the IDC report.
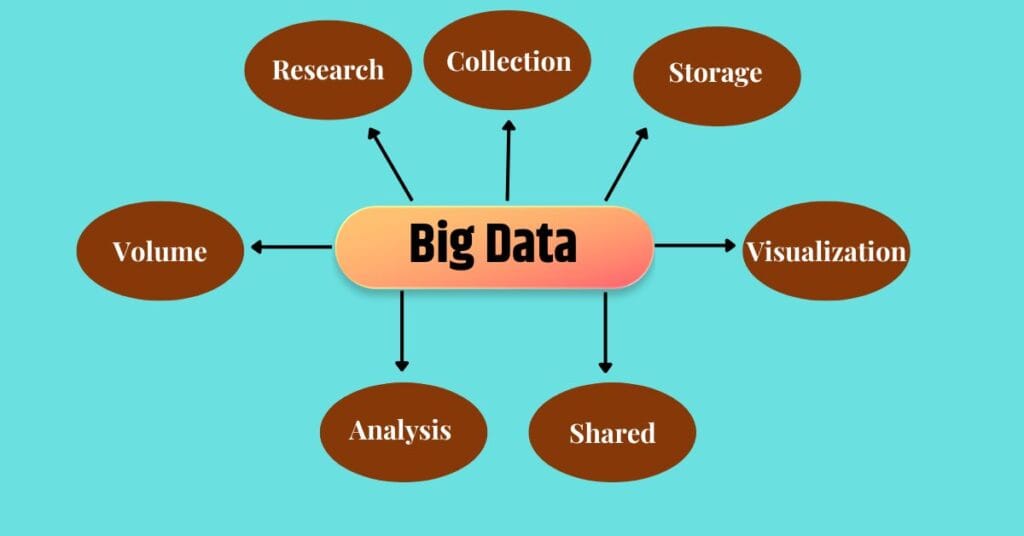
Characteristics of Big Data – Introduction Big Data
The defining traits of Big Data can be summarized using the 5 Vs:
- Volume: The sheer size of data generated daily is staggering. For instance, social media platforms like Facebook handle over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data daily, from user posts, images, and videos to comments and likes.
- Velocity: This refers to the speed at which data is generated and processed. Streaming platforms like Netflix analyze user preferences in real-time to recommend movies and shows, demonstrating how rapidly data can be utilized.
- Variety: Big Data comes in different formats:
● Structured Data: Databases, spreadsheets.
● Unstructured Data: Emails, social media posts, videos.
● Semi-structured Data: XML files, JSON data.
For example, a weather monitoring system collects data in diverse formats—temperature readings, satellite images, and written reports. - Veracity: This deals with the accuracy and reliability of data. Data from sources like surveys or social media can be misleading, making it crucial to validate and clean data before analysis.
- Value: The ultimate purpose of Big Data is to extract meaningful insights. For instance, e-commerce platforms like Amazon analyze shopping patterns to create personalized recommendations, driving customer satisfaction and sales.
Applications of Big Data – Introduction Big Data
- Healthcare: Hospitals use Big Data to predict disease outbreaks by analyzing patient records, social trends, and geographical data.
- Retail: Retailers utilize Big Data for inventory management, customer segmentation, and demand forecasting. Walmart, for instance, analyzes purchase history to stock products efficiently.
- Transportation: Ride-sharing apps like Uber analyze real-time traffic data, user demand, and driver availability to optimize ride prices and routes.
For your more information watch below video , Video Credit :- At A Glance!
Big Data is not just a trend; it is a transformative force reshaping industries. By effectively managing and analyzing vast amounts of data, organizations can unlock valuable insights, improve operations, and enhance customer satisfaction. As we move forward, embracing Big Data will be crucial for businesses to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world. Understanding its significance and applications will empower individuals and organizations to leverage its full potential, paving the way for innovation and growth. Big Data is transforming the way the world operates. By harnessing its power, businesses and organizations can uncover hidden opportunities, predict future trends, and solve critical challenges. Understanding the characteristics and types of Big Data is the first step toward appreciating its vast potential and leveraging it effectively in our digital-first world.
FAQ’s
What is Big Data?
Introduction Big Data, Big Data refers to the vast amounts of data generated daily, which is too large and complex for traditional data processing methods to handle.
How much data is created per person each second?
According to the IDC report, by 2020, each person was expected to generate 1.7 MB of data per second.
What is the projected total amount of global data by 2025?
The total amount of data worldwide is projected to reach 175 Zettabytes by 2025.
Why is data growth significant?
The rapid increase in data affects various sectors, including business analytics, healthcare, and technology, making data management and analysis critical.
How often does the total volume of data double?
The total volume of data is expected to double approximately every two years.