Motion in Real and Virtual Worlds: The Vestibular System
Vestibular System in Motion 2025 – Have you ever wondered how your body senses movement, balance, and orientation? Or why you might feel disoriented after using virtual reality (VR)? The answer lies in the vestibular system—a fascinating part of the human body that functions as an internal motion detector, keeping you steady and aware of your surroundings.

Vestibular System in Motion 2025
What Is the Vestibular System?
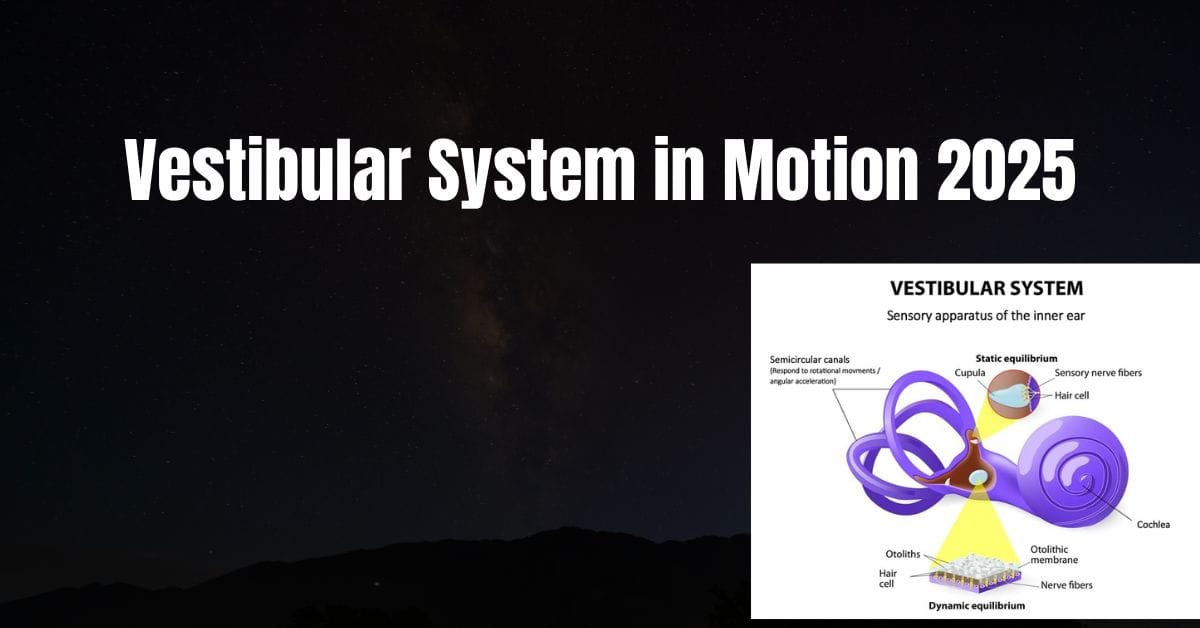
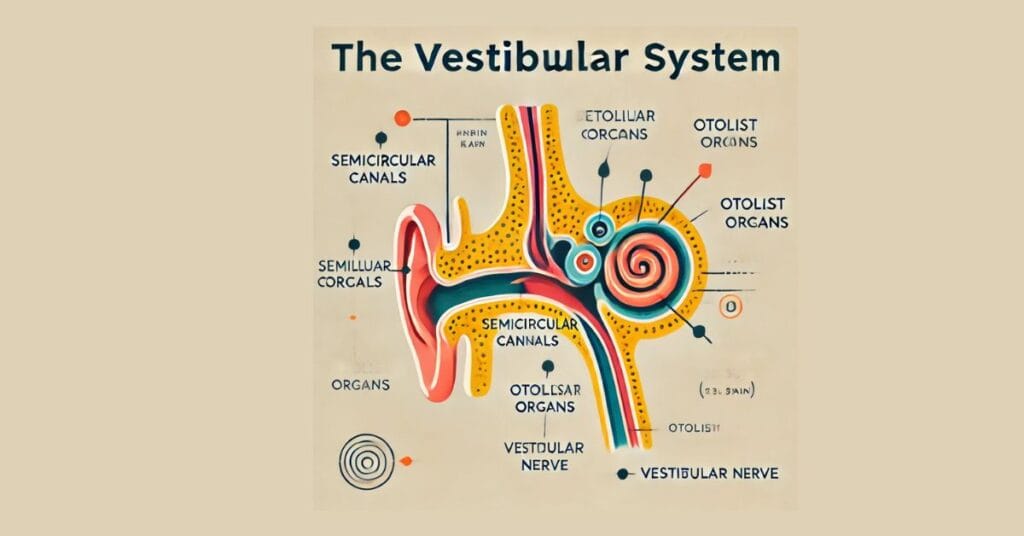
The vestibular system is a crucial part of the inner ear that helps you detect movement, maintain balance, and sense spatial orientation. It works hand-in-hand with your eyes, muscles, and brain to ensure you stay balanced and aware of your environment.
How It Works:
- Key Components in the Inner Ear:
- The semicircular canals: These three loop-shaped structures detect rotational movements, like nodding or turning your head.
- The utricle and saccule: These small organs sense linear movements, such as walking forward or tilting your head upward.
- Fluid and Sensory Hair Cells:
- The semicircular canals are filled with fluid. When you move your head, the fluid shifts, bending tiny hair-like structures called cilia. This bending sends signals to the brain, indicating the direction and speed of your movement.
- Crystals and Gravity:
- The utricle and saccule contain tiny crystals that shift with changes in position (e.g., standing up or lying down). These shifts trigger sensory signals to help your brain understand your orientation relative to gravity.
Motion in the Real World
In everyday life, the vestibular system works seamlessly to keep you balanced and coordinated. Here are some examples of how it functions:
- Walking:
- As you move, your vestibular system stabilizes your head and body, even on uneven surfaces.
- Turning Your Head:
- When you glance to the side or look up, the semicircular canals detect the rotation and help maintain your balance.
- Riding a Bike:
- The vestibular system ensures you remain upright while cycling, especially during turns or sudden stops.
- Recovering from a Slip:
- If you trip or stumble, your vestibular system quickly informs your brain of your body’s position, allowing you to regain stability.
Motion in Virtual Worlds – Vestibular System in Motion 2025
Virtual worlds aim to simulate real-world experiences, but this often creates challenges for the vestibular system. Let’s explore why:
1. Mismatch Between Vision and Balance:
- In VR, your eyes perceive movement (like a roller coaster ride), but your body remains stationary. This disconnect between visual input and vestibular sensations can cause motion sickness.
2. Lag or Delay:
- If there’s a delay between your physical movements and the corresponding VR display, your vestibular system may become confused, leading to discomfort.
3. Intense Movements:
- Sudden rotations, jumps, or rapid changes in VR games can overwhelm the vestibular system, causing dizziness or disorientation.
Vestibular System in Motion 2025
How Developers Mimic Motion in VR
To create immersive yet comfortable virtual experiences, developers use techniques that align with the vestibular system’s capabilities:
1. Adjusting Field of View (FOV):
- Reducing the FOV during fast-paced actions minimizes sensory overload and reduces motion sickness.
2. Head Tracking:
- VR headsets track head movements in real-time and adjust the virtual environment accordingly, creating a smoother experience for the vestibular system.
3. Gradual Acceleration:
- Simulating gradual motion instead of abrupt changes helps make virtual movements feel more natural.
4. Haptic Feedback:
- Vibrations in controllers or motion chairs provide physical cues that enhance the sense of motion, making it easier for the vestibular system to adapt.
Tips to Avoid Motion Sickness in VR
- Ease Into VR:
- Start with short sessions to allow your vestibular system to adjust.
- Use Comfort Settings:
- Many VR platforms offer options to reduce FOV, slow down movements, or limit rapid rotations.
- Stay Hydrated and Rested:
- A well-hydrated and rested body is better equipped to handle sensory challenges.
- Choose Stable Environments:
- Begin with VR experiences that involve minimal motion, like scenic walks or simple puzzle games.
- Take Regular Breaks:
- Pause whenever you feel discomfort, allowing your vestibular system time to recover.
Real-Life Applications of the Vestibular System in Virtual Worlds
- Training Simulators:
- Pilots and astronauts use VR simulators to train their vestibular systems for complex movements and environments.
- Medical Rehabilitation:
- VR helps patients with balance disorders improve their coordination and vestibular function.
- Gaming and Entertainment:
- Developers create immersive VR games that balance realism and comfort for the vestibular system.
- Sports and Fitness:
- VR workouts use motion simulation to make physical activities engaging and effective.
Why Study the Vestibular System?
Understanding the vestibular system is essential for creating better virtual experiences. For students and developers, knowledge of this system helps design VR applications that are immersive, realistic, and user-friendly. By working with the body’s natural systems, VR can enhance training, therapy, and entertainment.
Vestibular System in Motion 2025
The vestibular system is an extraordinary mechanism that allows us to move through the world with balance and ease. It plays a vital role in bridging the gap between real and virtual worlds. While VR presents unique challenges to this system, advances in technology and design are helping to create experiences that are both exciting and comfortable.
Vestibular System in Motion 2025 – FAQs
Q1: Why does VR sometimes cause dizziness?
The mismatch between visual motion and vestibular sensations can confuse your brain, leading to motion sickness.
Q2: Can VR improve balance in people with vestibular disorders?
Yes, VR is used in therapy to help patients retrain their vestibular systems and improve balance.
Q3: How do VR developers reduce motion sickness?
Techniques like real-time head tracking, limiting abrupt movements, and using haptic feedback make VR experiences smoother and more comfortable.
Vestibular System in Motion 2025
| For AR-VR Notes | Click Here |
| For Big Data Analytics (BDA) Notes | Click Here |