Introduction to Blockchain – Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that enables secure, transparent, and tamper-proof digital transactions. It is a decentralized ledger that records information in a way that is nearly impossible to alter, making it highly reliable for various applications.
Originally designed for Bitcoin in 2008 by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, blockchain has since evolved beyond cryptocurrencies. Today, it is widely used in finance, supply chain, healthcare, real estate, and even voting systems to ensure transparency and security.

What is a Blockchain?, Introduction to Blockchain
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers securely and transparently. Each block in the chain contains a set of transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block, ensuring data integrity and security. This technology eliminates the need for intermediaries, making transactions faster, more secure, and immutable.
Origin of Blockchain (Cryptographically Secure Hash Functions)
The foundation of blockchain technology lies in cryptographic principles, particularly hash functions. A cryptographic hash function is an algorithm that takes an input (data) and produces a fixed-size string of characters, which is unique to that data. Even a small change in the input results in a completely different hash, making it highly secure.
The concept of blockchain can be traced back to 1991, when Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta introduced a cryptographically secure chain of blocks for timestamping digital documents, ensuring they could not be tampered with. Later, in 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto applied these principles in Bitcoin’s whitepaper, creating the first decentralized blockchain.
Bitcoin vs. Blockchain: Understanding the Difference
Many people mistakenly believe that Bitcoin and Blockchain are the same, but they are not. While Bitcoin uses blockchain technology, blockchain itself is much broader and has applications beyond cryptocurrency.
1️⃣ What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records transactions securely and transparently. It can be used in various industries such as finance, healthcare, supply chain, real estate, and voting systems.
Key Features of Blockchain:
✅ Decentralized: No central authority controls it.
✅ Secure & Immutable: Transactions cannot be altered once recorded.
✅ Transparent: All participants can verify transactions.
✅ Used in Multiple Industries: Beyond cryptocurrency, blockchain is used in logistics, contracts, and data security.
2️⃣ What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a digital cryptocurrency that was introduced in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto. It is the first and most popular application of blockchain technology, allowing peer-to-peer transactions without a central authority like banks.
Key Features of Bitcoin:
✅ Built on Blockchain: Uses blockchain to record all transactions.
✅ Decentralized Currency: No government or bank controls it.
✅ Limited Supply: Only 21 million Bitcoins will ever exist.
✅ Used for Payments & Investment: People use Bitcoin for buying goods, transferring money, or as an investment.
3️⃣ Bitcoin vs. Blockchain: The Key Differences
| Feature | Blockchain | Bitcoin |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A decentralized ledger technology | A cryptocurrency built on blockchain |
| Use Cases | Finance, healthcare, supply chain, voting, smart contracts | Digital currency for transactions and investment |
| Control | Can be private or public | Fully decentralized and public |
| Functionality | Stores and secures digital records | Facilitates peer-to-peer transactions |
| Flexibility | Can be adapted for multiple industries | Specifically designed for cryptocurrency |
Key Characteristics of Blockchain
Blockchain is a game-changing technology that ensures secure, transparent, and tamper-proof digital record-keeping. It has three core characteristics:
1️⃣ Distributed: Blockchain is not controlled by a single entity but is spread across multiple computers (nodes) in a network. This decentralization prevents fraud and data loss.
2️⃣ Immutable: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be changed or erased. This ensures that all data remains accurate and tamper-proof.
3️⃣ Transparent: Every participant in the network can see and verify transactions, ensuring trust and accountability.
Physical Ledger Example vs. Blockchain
🔹 Traditional Physical Ledger (Example)
Imagine you buy flour from a shop on credit, and the shopkeeper writes the transaction in a physical ledger. However, the shopkeeper can later change the amount from ₹500 to ₹600, leading to a dispute since there’s no proof of the original amount.
🔹 Problem with Physical Ledgers
- They can be easily tampered with.
- There is no real-time verification.
- They rely on a single entity (shopkeeper) to maintain records.
How Blockchain Solves This Problem?
✅ Immutable Ledger: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it is permanent and cannot be changed. Each block is linked to the previous one, making it impossible to alter a record without modifying the entire chain.
✅ No Tampering Possible: If someone tries to change a transaction (e.g., modifying ₹500 to ₹600), the system immediately notifies all participants in the network, ensuring accountability.
✅ Real-Time Updates: Blockchain updates transaction records across all nodes in real-time. Everyone in the network has access to the same data, eliminating discrepancies and fraud.
How Does Blockchain Technology Work?
Bitcoin is a well-known application of blockchain technology, functioning as a decentralized cryptocurrency for exchanging digital assets online. Unlike traditional banking, Bitcoin transactions do not rely on third-party trust but instead use cryptographic proof for verification. Each transaction is secured through digital signatures and recorded on a public, immutable blockchain ledger. The Proof of Work (PoW) mechanism ensures secure validation through mining, where powerful computers solve complex mathematical puzzles to add transactions to the blockchain. With no central authority, low transaction costs, and global accessibility, Bitcoin offers a secure, transparent, and borderless financial system, revolutionizing digital payments.
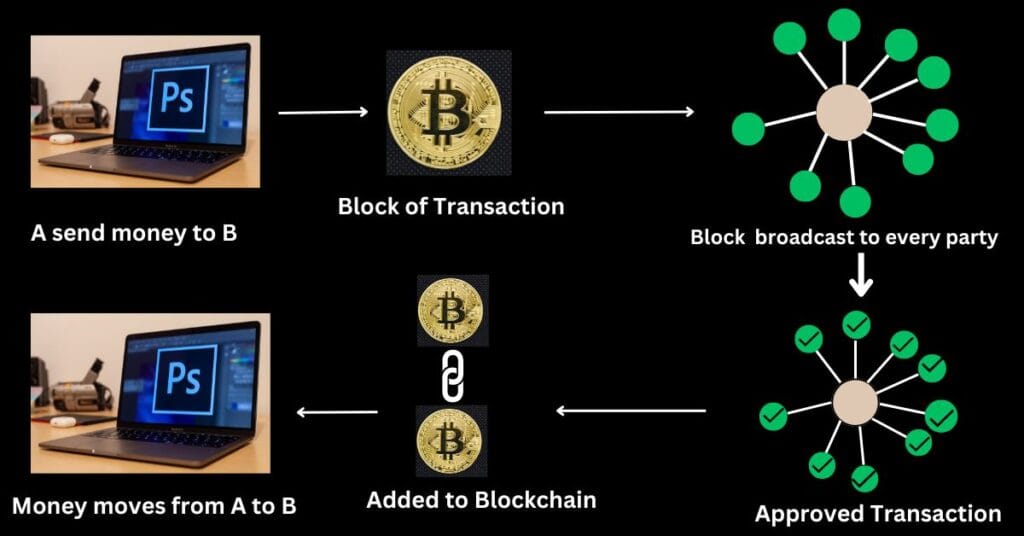
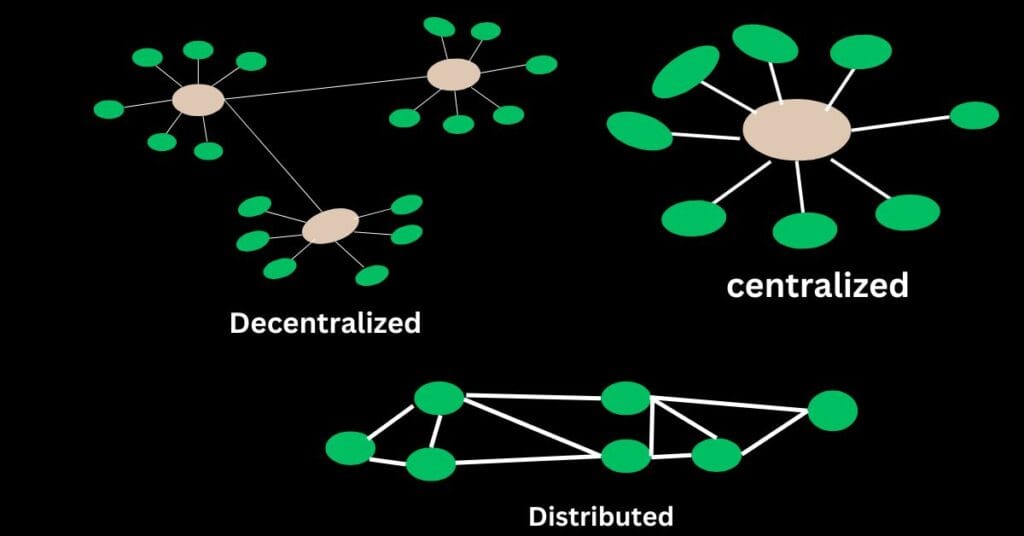
Blockchain Decentralization
Blockchain decentralization means that data is not stored on a central server but is distributed across millions of computers worldwide. This ensures security, transparency, and tamper-proof records, as every transaction is publicly verifiable and cannot be altered by a single entity.
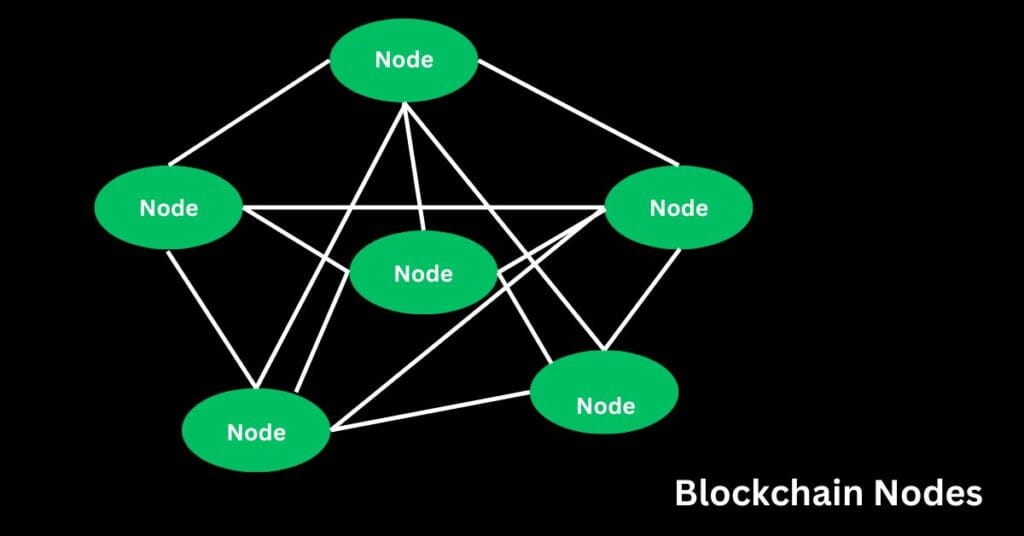
Blockchain nodes
A node is a computer that connects to the blockchain network. It uses a client to check and share transactions. When a node joins the blockchain, it downloads the latest data and stays up to date. Miners are special nodes that help confirm transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain, and they are rewarded with cryptocurrency for their work.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Decentralization: No central authority controls the data, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Security: Data is encrypted and linked, making it highly secure and resistant to tampering.
- Transparency: Transactions are publicly recorded and can be verified by all participants, promoting trust.
- Immutability: Once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted, ensuring a reliable history of transactions.
- Efficiency: Streamlined processes reduce the need for intermediaries, leading to faster and cheaper transactions.
- Accessibility: Anyone with internet access can participate in the blockchain network, enabling greater financial inclusion.
Disadvantages of Blockchain Technology
- Scalability Issues: As the network grows, transaction speeds can decrease, leading to delays and increased costs.
- Energy Consumption: Some consensus mechanisms, like Proof of Work, require significant energy and computational resources.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: The legal status of blockchain and cryptocurrencies varies by region, leading to compliance challenges.
- Complexity: Understanding and implementing blockchain technology can be complicated for businesses and users.
- Data Privacy Concerns: While transparency is an advantage, it may lead to privacy issues if sensitive data is stored on a public blockchain.
- Limited Adoption: Many industries are still exploring blockchain, and widespread adoption may take time.
Is blockchain secure ?
Yes, blockchain technology is considered secure for several reasons:
- Decentralization: Since data is distributed across a network of computers (nodes), there is no single point of failure or control, making it difficult for any malicious actor to alter the data.
- Cryptographic Security: Transactions are secured using cryptographic algorithms, which encrypt the data and ensure that only authorized users can access it. Each block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, linking them securely.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be changed or deleted without altering all subsequent blocks, which requires consensus from the majority of the network. This makes tampering nearly impossible.
- Consensus Mechanisms: Blockchain networks use consensus algorithms (like Proof of Work or Proof of Stake) to validate transactions, ensuring that only legitimate transactions are added to the blockchain.
- Transparency: All transactions are visible to network participants, allowing for independent verification and increasing accountability.
However, while blockchain itself is secure, vulnerabilities can arise from other factors, such as:
- Human Error: Mistakes in handling private keys or poorly designed smart contracts can lead to security breaches.
- 51% Attacks: If a single entity controls more than half of the network’s computing power, they could potentially manipulate transactions.
- Regulatory and Compliance Risks: As blockchain technology evolves, the regulatory landscape may pose risks to its security.
In summary, blockchain technology is fundamentally secure, but it is essential to implement best practices and maintain vigilance to address potential vulnerabilities.
| For AR-VR Notes | Click Here |
| For Big Data Analytics (BDA) Notes | Click Here |
FAQ’s
What is blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, secure digital ledger that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring transparency and immutability.
How does blockchain work?
Blockchain works by recording transactions in blocks, linking them together in a chain, and using cryptographic methods to secure and verify data.
Is blockchain secure?
Yes, blockchain is secure due to encryption, decentralization, and the use of consensus mechanisms, making it difficult to alter or tamper with data.
What is a node in blockchain?
A node is a computer connected to the blockchain network that validates and propagates transactions, maintaining a copy of the blockchain data.
What are the uses of blockchain?
Blockchain is used in cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin), supply chain management, healthcare, finance, and digital contracts, among other applications.

