Understanding Private Blockchain 2025: How It Works, Uses, and Benefits
Introduction
Understanding Private Blockchain 2025 – Blockchain technology is changing the way businesses store and share data. You might have heard about Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies that run on public blockchains. But did you know that there’s another type of blockchain that is private and used mainly by businesses? This is called a Private Blockchain.
What is a Private Blockchain?
A Private Blockchain is a type of blockchain that is controlled by a single organization or a group of authorized participants. Unlike public blockchains (where anyone can join), a private blockchain has restrictions on who can access and make changes to the data.
Think of it like a private club where only invited members can enter and participate. This makes it more secure and efficient for businesses that need privacy and fast transactions.
Key Characteristics of Private Blockchain
- Permissioned Access – Only authorized users can view and participate in transactions.
- Centralized Control – A single organization or a group of trusted participants manage the network.
- Fast Transactions – Since there are fewer participants, transactions are quicker than in public blockchains.
- Better Privacy – The data is not visible to the public, ensuring confidentiality.
- Efficient Governance – Organizations can set their own rules and permissions.
Need for Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are essential for organizations that require:
- Data security – Protection of sensitive information.
- Fast processing – Quick verification of transactions.
- Regulatory compliance – Meeting industry standards.
- Cost efficiency – Lower costs compared to public blockchains.
- Controlled access – Ensuring only trusted parties can make changes.
How Does Private Blockchain Work?
Private blockchains operate similarly to public blockchains but with additional control and security. Here’s how they function:
- Data Storage – Information is stored in blocks linked together securely.
- Permissioned Nodes – Only selected nodes (computers) can participate in the network.
- Smart Contracts – Automated agreements ensure transactions are executed based on predefined rules.
- Consensus Mechanisms – Transactions are validated using efficient algorithms like PAXOS or RAFT instead of energy-intensive mining.
- State Machine Replication – Ensures all authorized users maintain the same copy of data, making it tamper-proof.
Example: Imagine a bank using a private blockchain for recording customer transactions. Only the bank’s employees and authorized regulators can access the system, ensuring privacy and security.
Smart Contracts in a Private Environment
Smart contracts in private blockchains automate transactions between trusted parties. These contracts execute automatically when predefined conditions are met, ensuring transparency and efficiency.
Example: In supply chain management, a smart contract can release payment to a supplier once goods are delivered and verified.
Consensus Algorithms for Private Blockchain
Private blockchains use efficient consensus algorithms that ensure data integrity and security without requiring extensive computational power.
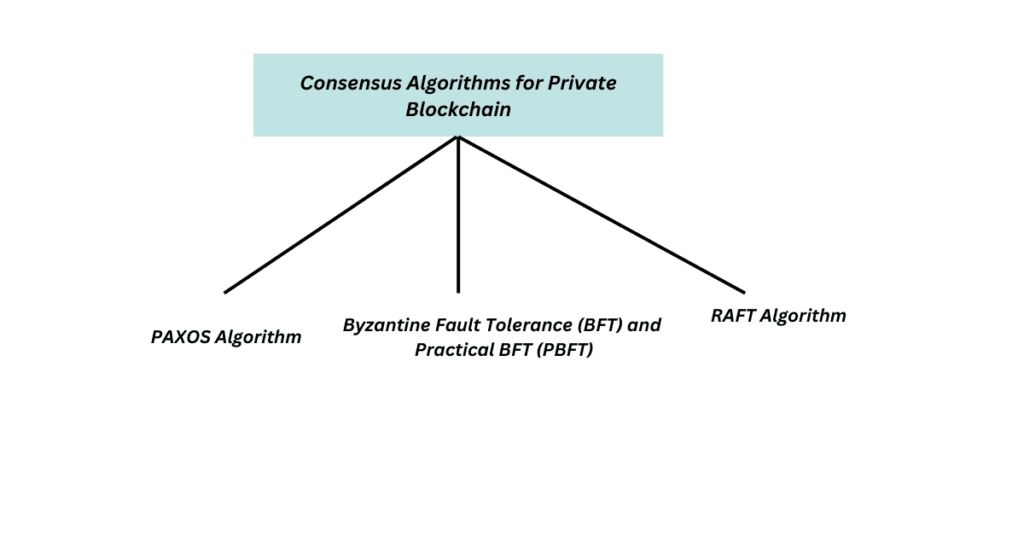
1. PAXOS Algorithm
- A fault-tolerant consensus mechanism.
- Ensures that all nodes in a network agree on a single version of data.
- Used in enterprise systems for reliability.
2. RAFT Algorithm
- A leader-based consensus mechanism.
- Ensures smooth data replication across nodes.
- Faster and more efficient than traditional methods.
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) and Practical BFT (PBFT)
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) ensures that a blockchain network remains secure even if some nodes act maliciously.
- BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerance): The network can function properly even if some participants fail or provide incorrect information.
- PBFT (Practical BFT): A more efficient version of BFT, reducing transaction delays while maintaining security.
Example: Financial institutions use PBFT in private blockchains to maintain trust and data integrity.
Uses of Private Blockchain
Private blockchains are widely used in industries that require security, efficiency, and control over data. Here are some common applications:
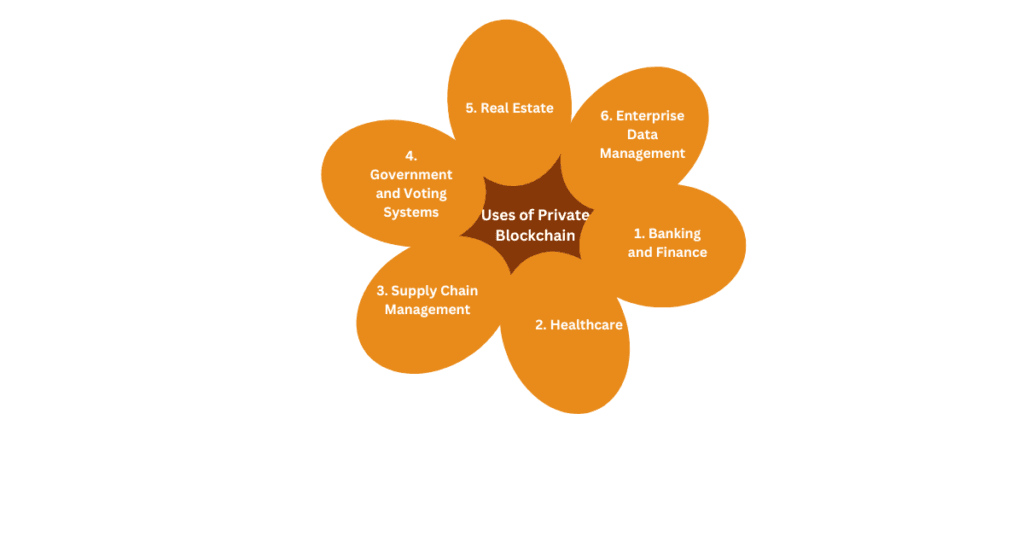
1. Banking and Finance
- Example: Banks use private blockchains to speed up transactions and reduce fraud.
- Helps in cross-border payments, loan approvals, and secure data storage.
2. Healthcare
- Example: Hospitals store patient records on private blockchains, allowing only doctors and authorized staff to access them.
- Helps in reducing errors and protecting sensitive medical data.
3. Supply Chain Management
- Example: Companies like Walmart use private blockchains to track the movement of goods.
- Ensures authenticity and prevents fraud in supply chains.
4. Government and Voting Systems
- Example: Governments use private blockchains to manage citizen records, taxes, and land ownership.
- Helps in conducting secure and tamper-proof elections.
5. Real Estate
- Example: Property ownership records stored on a private blockchain prevent fraud.
- Eliminates the need for paper documents and speeds up transactions.
6. Enterprise Data Management
- Example: Companies use private blockchains to store contracts, employee data, and financial records securely.
- Ensures that only authorized individuals have access.
Advantages of Private Blockchain
Private blockchains offer several benefits, making them ideal for businesses and organizations:
- Faster Transactions – Fewer participants mean quicker processing times.
- Enhanced Security – Only authorized users can access data, reducing hacking risks.
- Lower Costs – No need for expensive public blockchain validation processes.
- More Control – Organizations can set their own rules and permissions.
- Better Compliance – Easier to meet regulatory requirements compared to public blockchains.
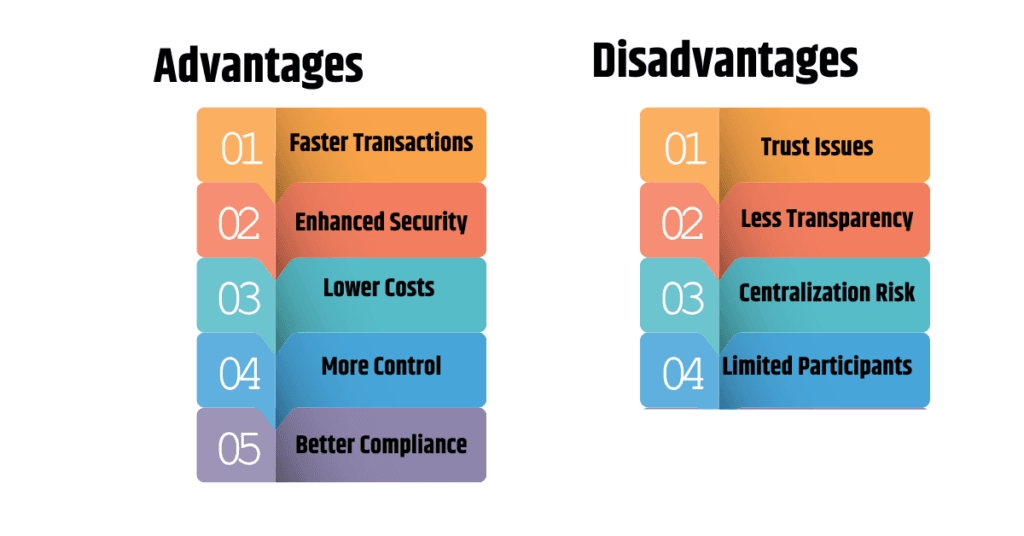
Disadvantages of Private Blockchain
While private blockchains offer many benefits, they also come with some drawbacks:
- Less Transparency – Since it is controlled by a single organization, there is less public accountability.
- Centralization Risk – If the central authority is compromised, the entire network may be affected.
- Limited Participants – Only approved users can join, reducing decentralization.
- Trust Issues – Users must trust the organization managing the blockchain.
Understanding Private Blockchain 2025 – FAQs
1. How is private blockchain different from public blockchain?
Public blockchains are open to everyone, while private blockchains have restricted access.
2. Is private blockchain more secure than public blockchain?
Yes, since access is limited, it is less prone to hacking and unauthorized changes.
3. Can private blockchain be hacked?
It is difficult but possible if the central authority is compromised.
4. Do private blockchains use cryptocurrencies?
Not always. Many private blockchains are used for data management rather than digital currencies.
5. Which companies use private blockchain?
Major companies like IBM, Microsoft, and Walmart use private blockchain for secure transactions.
Summary
Private blockchains are ideal for businesses that need fast, secure, and controlled access to data. Unlike public blockchains, they offer more privacy, efficiency, and regulatory compliance. However, they also come with challenges such as centralization and trust issues. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, private blockchains will play a key role in industries like finance, healthcare, and supply chain management.
Comparison Between Bitcoin and Ethereum 2025
How to Use Blockchain Domains 2025
Understanding Smart Contracts in Blockchain 2025
Hey everyone! If you have any questions or thoughts, feel free to drop a comment. Let’s learn and discuss together. Your feedback is always welcome!