Blockchain is a secure and transparent way to store and share data. It reduces fraud, improves efficiency, and builds trust across industries. As digital transactions grow, blockchain offers a reliable solution for the future.
Blockchain technology has emerged as a game-changer in the digital world, revolutionizing how data is stored, shared, and secured.

It is a decentralized and immutable ledger that ensures transparency, security, and trust in various applications.
From finance and healthcare to supply chain and cybersecurity, blockchain is transforming industries by reducing fraud, enhancing efficiency, and improving data integrity.
Characteristics of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has several defining characteristics that set it apart from traditional systems:
Decentralization
Unlike conventional databases controlled by a single authority, blockchain operates on a peer-to-peer network. This means no single entity has control over the entire system, making it more secure and resistant to fraud or hacking attempts.
Transparency
Blockchain Technology- Every transaction on the blockchain is recorded in a way that all participants can verify. This fosters trust and accountability, as no hidden alterations can be made.

Immutability
in Blockchain Technology Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This tamper-proof nature ensures data integrity, making blockchain ideal for storing sensitive information such as medical records, contracts, and financial transactions.
Security
Blockchain uses advanced cryptographic techniques, including hashing and digital signatures, to secure data. These security measures protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Consensus Mechanisms
in Blockchain Technology Transactions on a blockchain are validated through consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms prevent unauthorized modifications and maintain the integrity of the ledger.
How Blockchain Technology Enhances Data Sharing
Sharing data between organizations has traditionally been a slow and insecure process. Blockchain technology addresses these challenges by:
- Ensuring Data Integrity: Once data is entered, it remains unchanged, reducing errors and fraud.
- Providing Real-Time Access: Businesses can instantly verify and share information, improving collaboration and decision-making.
- Reducing Intermediaries: Blockchain removes the need for third parties, lowering costs and enhancing efficiency.
- Enhancing Security: Cryptographic encryption ensures data privacy and prevents cyber threats.
The Role of Hashing in Blockchain Security
A hash is a cryptographic function that converts data into a fixed-length string. Hashing plays a crucial role in blockchain security by:
- Maintaining Data Integrity: Even a small change in the input results in a completely different hash, making tampering evident.
- Enhancing Security: Hash functions like SHA-256 create unique identifiers for each transaction, making blockchain highly secure.
- Preventing Fraud: Hashing prevents duplicate transactions and unauthorized modifications.
Blockchain in Accounting
Blockchain Technology is reshaping accounting by improving transparency and efficiency. Key benefits include:
- Automating Transactions: Smart contracts execute transactions automatically when conditions are met.
- Enhancing Transparency: Every financial transaction is recorded permanently, reducing fraud.
- Simplifying Audits: Auditors can verify transactions directly on the blockchain, making the process faster and more reliable.
- Lowering Costs: Businesses can eliminate intermediaries, reducing transaction fees and reconciliation expenses.
blockchain internet of things
Blockchain and the Internet of Things (IoT) – A Powerful Combination for the Future
Imagine a world where all your smart devices—phones, cars, home appliances, and even factory machines—communicate seamlessly without security risks. That’s the promise of the Internet of Things (IoT).

However, with billions of connected devices, security and data privacy have become major concerns. This is where blockchain steps in, offering a decentralized and secure way to manage IoT data.
Why IoT Needs Blockchain
IoT devices constantly collect and exchange data, but most of this data is stored on centralized servers, making them easy targets for hackers.
Cyberattacks on smart home systems, medical devices, and even industrial machines are becoming more common. Blockchain, a tamper-proof digital ledger, ensures that data is stored securely, preventing unauthorized access and fraud.
How Blockchain Enhances IoT
- Security & Transparency: Blockchain makes sure IoT data cannot be altered or hacked.
- Automation with Smart Contracts: Devices can interact and execute tasks without human intervention.
- Reduced Costs: Eliminating intermediaries in IoT networks cuts costs and increases efficiency.
How Blockchain is Changing Renewable Energy
Imagine a world where you can generate your own solar power and sell the extra energy to your neighbor without going through a big utility company. Sounds amazing, right? That’s exactly what blockchain is making possible in the renewable energy sector.
Blockchain, a secure and transparent digital ledger, is revolutionizing how we produce, trade, and consume energy. With the world moving toward cleaner energy sources like solar and wind, blockchain helps ensure fair pricing, cuts out the middleman, and makes the whole system more efficient.
What is Blockchain, and How Does It Work?
Think of blockchain as a digital notebook that everyone can see but no one can erase or tamper with. Every time a transaction happens—like selling extra solar energy to a neighbor—it gets recorded in this notebook permanently. No single company controls it, making the system decentralized and more trustworthy.
Because of this transparency, blockchain helps eliminate fraud, speeds up transactions, and reduces costs, making it a perfect fit for the energy industry.
The Problems in Renewable Energy Today
Despite the growing use of solar panels and wind farms, the energy sector still has some big issues:

- Big corporations control the energy grid, leaving consumers with little say.
- Lack of transparency makes it hard to know if you’re really getting green energy.
- High costs make switching to renewable energy difficult for many people.
How Blockchain Solves These Problems
With blockchain, individuals can trade energy directly with each other instead of relying on utility companies. It ensures fair pricing, makes transactions faster, and keeps energy distribution more efficient.
Peer-to-Peer Energy Trading: The Future of Power
Blockchain allows people with solar panels or wind turbines to sell extra energy directly to their neighbors. Projects like Brooklyn Microgrid and Power Ledger are already making this a reality, proving that the future of energy is decentralized, fair, and efficient.
Blockchain is not just a buzzword—it’s a game changer for the renewable energy world!
Blockchain for Data Storage: A Secure and Decentralized Future
Data is the backbone of the digital world, but storing it securely has become a growing challenge. With cyberattacks, data breaches, and centralized servers at risk of failure, traditional data storage methods have significant drawbacks. This is where blockchain technology steps in.
Blockchain offers a decentralized, tamper-proof way to store data securely, making it a game-changer for businesses, governments, and individuals looking for better data management solutions.
How Traditional Data Storage Works
Most organizations store data in centralized servers or cloud storage systems. While convenient, these methods come with risks:
- Hacking and Data Breaches – Centralized databases are prime targets for cybercriminals.
- Server Failures – If a central server crashes, valuable data can be lost.
- Lack of Transparency – Users have little control over how their data is stored and used.
What is Blockchain-Based Data Storage?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records and stores data across multiple nodes (computers) instead of a single central server. Each piece of data is encrypted, timestamped, and linked to the previous block, ensuring security and transparency.
Unlike traditional storage, blockchain doesn’t rely on a single entity, making it resistant to hacks and system failures.
Key Benefits of Blockchain for Data Storage
1. Enhanced Security
Blockchain encrypts and distributes data across multiple nodes, making it nearly impossible for hackers to alter or steal information.
2. Decentralization
Instead of storing data in one place, blockchain distributes it across a network, eliminating single points of failure.
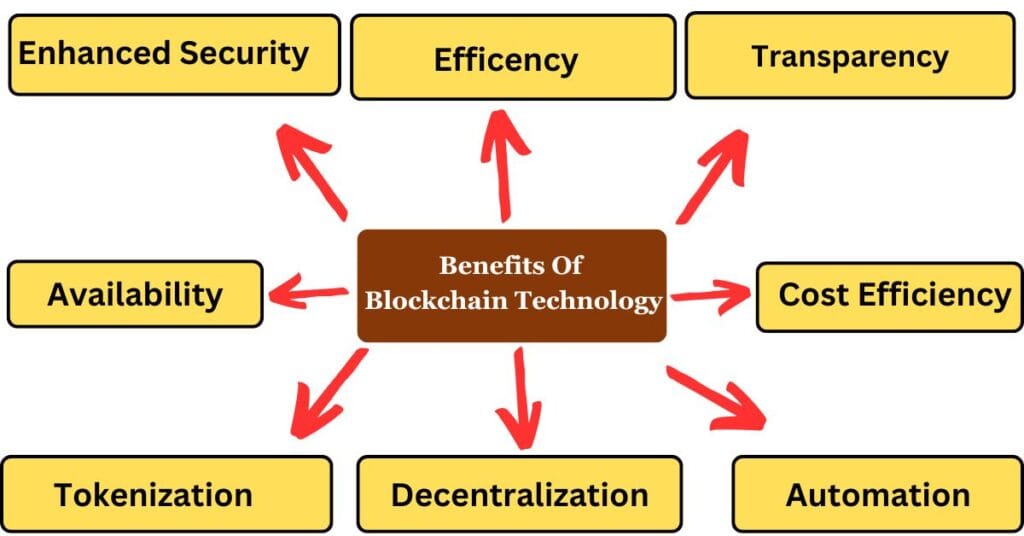
3. Transparency and Immutability
Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, ensuring trust and transparency.
4. Cost Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and reducing server maintenance costs, blockchain storage can be more cost-effective than traditional cloud storage solutions.
Real-World Use Cases of Blockchain for Data Storage
- Healthcare – Securely storing and sharing patient records while maintaining privacy.
- Finance – Protecting sensitive financial transactions and documents from fraud.
- Government – Storing public records, voting data, and land registries securely.
- Enterprises – Ensuring secure collaboration and storage of corporate data.
The Future of Blockchain in Data Storage
As technology advances, blockchain-based storage solutions will continue to evolve, offering even greater security, efficiency, and transparency. With companies like Filecoin, Storj, and Sia leading the way, the future of data storage is decentralized and secure.
Blockchain isn’t just about cryptocurrencies—it’s a revolutionary way to store and protect data in the digital age!
Blockchain Security Issues: Challenges and Risks in Decentralized Systems
Blockchain is often praised for its security, but is it truly unbreakable? While the technology offers decentralization, transparency, and immutability, it’s not without risks. Security vulnerabilities in blockchain networks can lead to hacking, fraud, and system failures. Understanding these issues is crucial for ensuring the safety of blockchain applications.
Common Security Issues in Blockchain
1. 51% Attack
A 51% attack happens when a group of miners gains control of more than 50% of a blockchain’s computing power. This allows them to:
- Reverse transactions (double-spending).
- Prevent new transactions from being verified.
- Manipulate the blockchain’s history.
This threat is more significant for smaller blockchains with lower mining power.
2. Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are self-executing programs on a blockchain. However, poorly written code can lead to:
- Exploitable bugs (as seen in the DAO hack, where $60 million was stolen).
- Permanent loss of funds due to coding errors.
- Unauthorized access and manipulation of contracts.
3. Private Key Theft
Blockchain relies on cryptographic keys for access. If a private key is lost or stolen:
- The user permanently loses access to their assets.
- Hackers can steal cryptocurrencies and sensitive data.
- There’s no way to recover stolen funds, as transactions are irreversible.
4. Phishing Attacks
Hackers often use phishing to trick users into revealing their private keys or login credentials. Common tactics include:
- Fake wallet apps.
- Fraudulent websites mimicking exchanges.
- Emails and messages pretending to be from legitimate blockchain companies.
5. Sybil Attacks
In a Sybil attack, hackers create multiple fake identities (nodes) in a blockchain network to manipulate transactions or disrupt the system. This can lead to:
- Slower transaction verification.
- Control over decision-making in decentralized networks.
6. Centralization Risks in Some Blockchains
While blockchain is designed to be decentralized, some networks rely on a few large mining pools or validators. If too much control is concentrated in a few hands, it creates:
- A risk of collusion and manipulation.
- Potential censorship of transactions.
- Reduced security and trust in the system.
Difference between Blockchain and Database
Here is a table comparing Blockchain and Database –
Here is a table comparing Blockchain and Database:
| Feature | Blockchain | Database |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Data stored in blocks linked together | Data stored in tables like spreadsheets |
| Control & Authority | Decentralized, no single entity controls it | Centralized, controlled by an administrator |
| Security | Uses cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms | Uses authentication mechanisms like passwords & encryption |
| Immutability | Data cannot be altered or deleted | Data can be modified or deleted by authorized users |
| Transparency | Often public, allowing anyone to verify transactions | Restricted access, controlled by the owner |
| Performance & Speed | Slower due to validation and consensus processes | Faster as no consensus mechanism is required |
| Scalability | Limited scalability due to decentralized verification | Highly scalable, suitable for large applications |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrencies, supply chains, smart contracts, DeFi | Banking, e-commerce, social media, corporate data management |
How to Improve Blockchain Security
- Use Strong Smart Contract Audits – Companies should audit smart contract code before deployment.
- Decentralize Mining and Validation – Encouraging distributed mining helps prevent 51% attacks.
- Implement Multi-Signature Wallets – Requiring multiple keys for transactions adds security.
- Enhance User Awareness – Educating users about phishing and scams reduces human errors.
- Use Secure Key Management – Storing private keys in offline (cold) wallets prevents hacks.
Cryptography in Cybersecurity
Cyber threats are increasing every day, making data security more important than ever. Cryptography helps protect information by turning it into unreadable code, allowing only authorized people to access it.
It is used in banking, messaging apps, and password protection to keep data safe from hackers.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is a method of securing information by using special codes. It ensures:
- Privacy – Only the intended person can read the data.
- Security – Prevents unauthorized changes to the data.
- Verification – Confirms the identity of the sender and receiver.
Types of Cryptography
Secret Key Encryption
- Uses one key to lock and unlock data.
- Fast but risky if the key is stolen.
- Example: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard).
Public & Private Key Encryption
- Uses two keys: one for locking data and another for unlocking it.
- More secure but slower.
- Example: RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman).
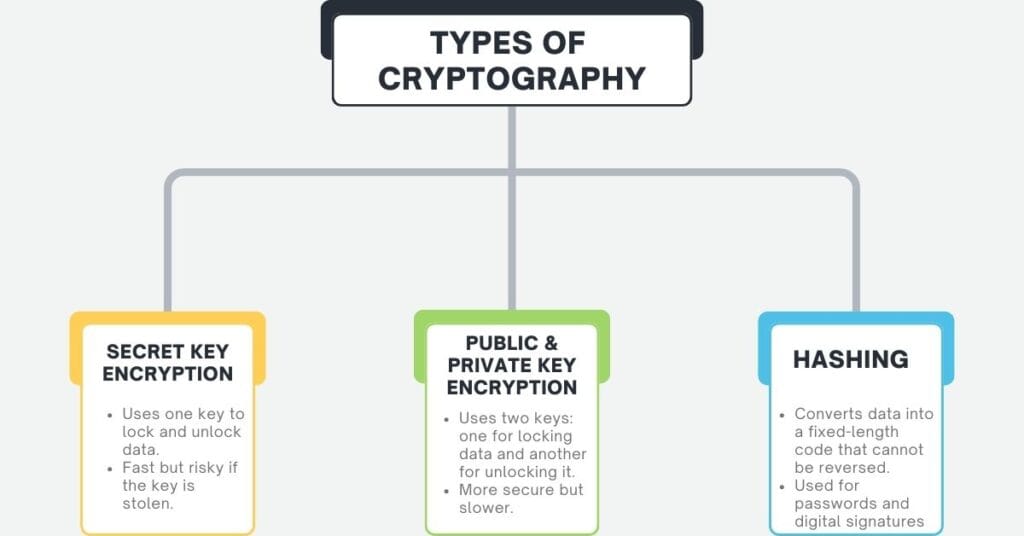
Hashing
- Converts data into a fixed-length code that cannot be reversed.
- Used for passwords and digital signatures.
- Example: SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm).
How Cryptography Protects Data
Secure Messaging
Apps like WhatsApp and Signal use encryption to keep chats private.
Safe Online Payments
Cryptography protects credit card details and bank transactions.
Strong Password Security
Websites store passwords in an unreadable format to prevent hacking.
Digital Signatures
Used to verify documents and prevent forgery.
Protecting Cryptocurrency
Bitcoin and other digital currencies use cryptography to secure transactions.
Challenges in Cryptography
- Future Threats – Quantum computers may break current encryption methods.
- Weak Passwords – Poor key management can make encryption useless.
- Government Access – Some authorities try to bypass encryption for surveillance.
Blockchain is a digital system that records transactions securely and transparently. Instead of relying on a central authority like a bank, it works through a network of computers.
How Blockchain Works:
- Every transaction is stored in a “block.”
- These blocks are linked together like a chain, making data nearly impossible to change or hack.
- The system is decentralized, meaning no single entity controls it.
Key Advantages:
- Transparency: Everyone in the network can see and verify transactions.
- Security: Uses advanced encryption to prevent fraud and hacking.
- Efficiency: Eliminates middlemen, making transactions faster and cheaper.
Applications of Blockchain:
- Banking: Speeds up money transfers and reduces fraud.
- Supply Chain: Helps track products from factories to customers.
- Healthcare: Protects patient records and ensures data privacy.
- Government: Used for secure voting and identity verification.
Challenges of Blockchain:
- High Energy Consumption: Some systems require a lot of electricity.
- Regulatory Issues: Governments are still figuring out laws for blockchain.
Despite these challenges, blockchain technology is improving. As advancements continue, it will likely become more efficient and widely used, making everyday transactions safer and smoother.
Blockchain Analysis and Future Trends
Blockchain is more than just a digital ledger; it is a transformative force with far-reaching implications. A detailed analysis reveals:
Technical Structure
Blockchain consists of a series of blocks, each containing transaction data, timestamps, and cryptographic hashes, ensuring data security and transparency.
Comparison with Traditional Databases
Unlike centralized databases, blockchain offers decentralized security and immutability, making it a more trustworthy alternative.
Future Trends
- Hybrid Blockchains: Combining public and private blockchains for enhanced security and efficiency.
- Interoperability: Seamless communication between different blockchain networks.
- Sustainability Solutions: Energy-efficient consensus mechanisms to reduce blockchain’s carbon footprint.
for more information watch below video – video credit : Accenture
Pros and Cons of Blockchain Technology
Pros:
- High Security: Cryptographic encryption makes transactions tamper-proof.
- Transparency: Every transaction is permanently recorded and verifiable.
- Decentralization: Eliminates single points of failure, reducing hacking risks.
- Fast Transactions: Reduces reliance on intermediaries, speeding up processing times.
- Fraud Prevention: Immutable records prevent data tampering and unauthorized changes.
- Cost Reduction: Eliminates intermediaries, lowering transaction fees.
Cons:
- High Energy Consumption: PoW blockchains require significant computing power.
- Scalability Issues: Large networks may experience slower processing speeds.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Different jurisdictions have varying blockchain regulations.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Public blockchains expose transaction details to all participants.
- Implementation Complexity: Businesses need technical expertise to integrate blockchain solutions effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the four types of blockchain technology?
The four main types of blockchain are Public, Private, Consortium, and Hybrid blockchains.
Can you give an example of blockchain technology?
Bitcoin is a well-known example of blockchain technology used for decentralized digital transactions.
How does Amazon use blockchain?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides managed blockchain services to help businesses develop scalable blockchain applications.
Who invented blockchain?
Blockchain was introduced by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2008 as the underlying technology for Bitcoin.
How is blockchain used in cybersecurity?
Blockchain enhances cybersecurity by providing encrypted, tamper-proof data storage and decentralized authentication.
What are the biggest challenges facing blockchain technology?
Scalability, regulatory issues, energy consumption, and adoption barriers are among the biggest challenges.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is reshaping industries by improving security, transparency, and efficiency. From secure financial transactions to supply chain optimization and healthcare data management, blockchain’s impact is undeniable.
While challenges such as scalability and regulatory concerns remain, ongoing advancements promise a more secure, decentralized future. Businesses and individuals must stay informed and adapt to blockchain’s potential to fully harness its benefits.

