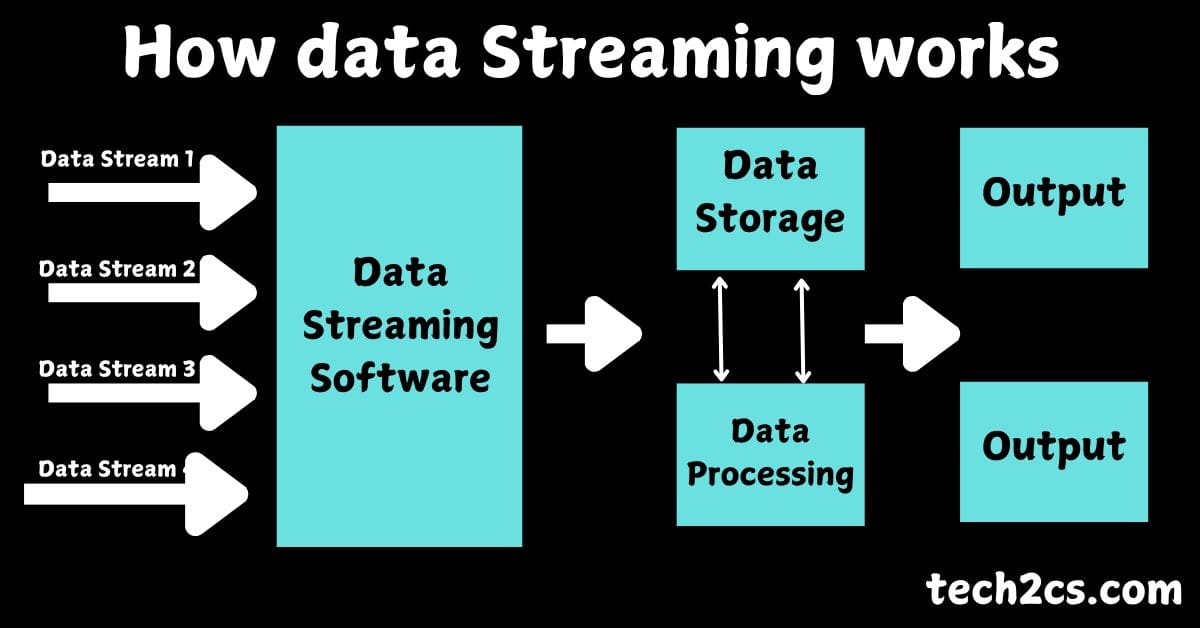
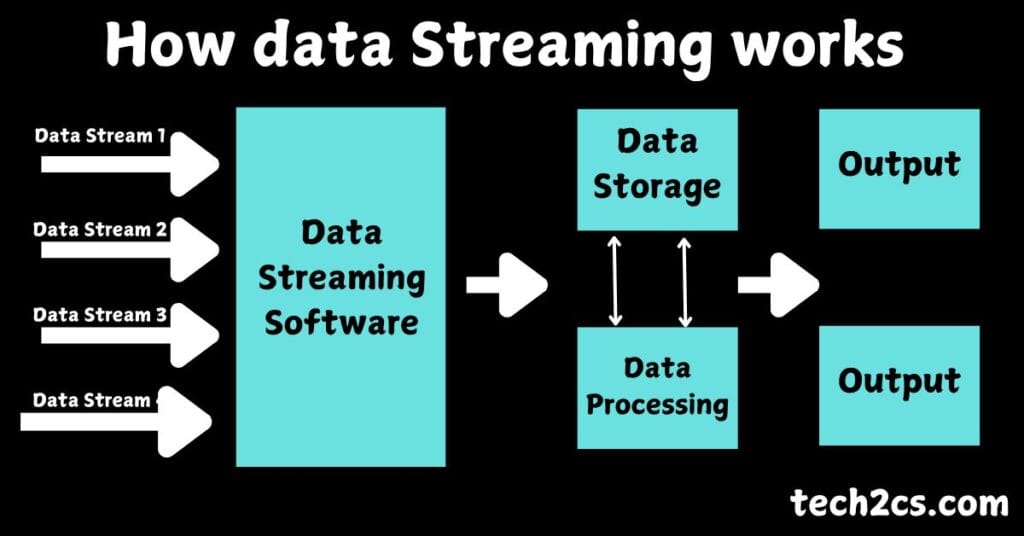
Data Streams in Data Analytics – Data streams are an integral part of modern data analytics, enabling real-time insights and decision-making. This blog explores the concept of data streams, their components, benefits, and how they are reshaping the analytics landscape.
What Are Data Streams?
A data stream is a continuous flow of data generated in real-time from various sources such as IoT devices, social media platforms, financial transactions, sensors, and more. Unlike traditional batch data, streams are processed as they arrive, making them ideal for time-sensitive applications.
Components of Data Streams
- Data Sources – These include sensors, logs, user interactions, or any system that generates data in real-time.
- Stream Ingestion – Tools like Apache Kafka, Amazon Kinesis, or Google Cloud Pub/Sub are used to collect and forward data streams for processing.
- Stream Processing – Frameworks such as Apache Flink, Apache Spark Streaming, and Azure Stream Analytics help process and analyze data on the fly.
- Storage – Data streams can be stored in databases or data lakes for long-term analysis using technologies like Amazon S3 or HDFS.
- Visualization and Insights – Dashboards and analytics tools display insights in real-time, supporting decision-making.
Sources of Data Streams | Data Streams in Data Analytics
Data streams can originate from a wide range of sources depending on the industry and application. Here’s a detailed look at the most common sources of data streams:
1. Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
IoT devices are one of the primary sources of real-time data streams. These include:
- Sensors: Temperature, humidity, pressure, and motion sensors.
- Wearables: Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitoring devices.
- Smart Appliances: Connected devices like refrigerators, washing machines, and home assistants.
2. Social Media Platforms
Social media generates vast amounts of real-time data, including:
- Posts and Comments: User-generated content on platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.
- Likes, Shares, and Reactions: Engagement metrics that provide insights into trends and sentiments.
- Streaming Video and Audio: Real-time user interaction data from platforms like YouTube, TikTok, and Spotify.
3. Financial Transactions
The financial sector relies on continuous data streams for:
- Stock Market Feeds: Real-time stock prices, trading volumes, and market indices.
- Payment Gateways: Transactions from services like PayPal, Stripe, or credit card networks.
- Cryptocurrency Exchanges: Real-time updates on cryptocurrency prices and trades.
4. Mobile Applications
Mobile apps generate data streams through:
- User Interactions: Clicks, scrolls, and searches within the app.
- Location Data: Real-time GPS data for navigation, delivery tracking, or ride-sharing.
- Notifications: User engagement metrics from app alerts and messages.
5. Streaming Services
Data streams are central to media and entertainment platforms, including:
- Video Services: Real-time viewership data from platforms like Netflix and Amazon Prime.
- Music Platforms: Listener habits and preferences on services like Spotify or Apple Music.
- Live Streams: Interaction and performance data during live events or broadcasts.
6. Web Logs and Clickstreams
Websites and e-commerce platforms track user behavior in real-time via:
- Web Server Logs: Logs of user activity on websites.
- Clickstreams: Sequential data of user navigation paths, clicks, and purchases.
- Ad Impressions: Real-time metrics from digital ad campaigns.
7. Communication Systems
Real-time communication services provide data streams through:
- Chats and Messaging: Platforms like WhatsApp, Slack, or Microsoft Teams.
- VoIP Calls: Data from voice calls using services like Skype or Zoom.
- Email Systems: Email open rates and engagement metrics.
8. Industrial Systems
Industries generate data streams from:
- SCADA Systems: Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition for industrial automation.
- Machines and Equipment: Telemetry from manufacturing equipment and robotics.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Real-time tracking of shipments and inventory.
9. Healthcare Systems
Healthcare providers use data streams for:
- Medical Devices: Data from heart monitors, glucose sensors, and ventilators.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Updates to patient records in real time.
- Emergency Systems: Live updates from ambulances or critical care units.
10. Public and Environmental Data
Government and environmental monitoring systems generate streams like:
- Traffic Sensors: Real-time traffic flow and congestion data.
- Weather Stations: Updates on temperature, wind, and rainfall.
- Earth Observation Satellites: Geospatial data for climate analysis.
11. Gaming Platforms
Gaming companies stream data for:
- Player Interactions: Real-time activity logs from online games.
- Leaderboards: Live updates of player rankings and scores.
- Esports Events: Streaming audience engagement metrics.
Applications of Data Streams
- IoT Analytics – Real-time monitoring of IoT devices helps in predictive maintenance and smart automation.
- Financial Services – Stream processing aids fraud detection, stock price analysis, and high-frequency trading.
- Social Media Analytics – Analyzing user interactions to detect trends and sentiments as they occur.
- Healthcare – Real-time patient monitoring improves emergency response and treatment efficiency.
- Supply Chain and Logistics – Data streams optimize inventory, track shipments, and predict delays.
Benefits of Data Streams in Analytics
- Real-Time Decision Making – Organizations can respond to events as they occur, reducing delays in actions.
- Improved Scalability – Stream processing frameworks are designed to handle massive amounts of data efficiently.
- Enhanced Customer Experience – Personalized recommendations and instant feedback improve user satisfaction.
- Cost-Effectiveness – Processing data in motion reduces storage costs and increases operational efficiency.
- Accuracy and Relevance – Streaming ensures data is always up-to-date, improving the reliability of insights.
Challenges in Handling Data Streams
- High Throughput Requirements – Managing massive volumes of data in real-time demands robust infrastructure.
- Data Quality Issues – Ensuring the accuracy and completeness of continuous data streams can be challenging.
- Latency – Minimizing delays in data processing requires fine-tuned systems.
- Integration – Seamlessly connecting various data sources and platforms is a complex task.
- Security Concerns – Protecting sensitive information within live streams is critical.
Future of Data Streams in Analytics
- Real-Time AI Integration: Advanced AI and machine learning models will process streams in real time for predictive analytics and autonomous systems.
- Edge Computing: Data processing closer to the source will reduce latency, enhance IoT efficiency, and support real-time decision-making.
- 5G and Connectivity: Faster networks will support high-speed, large-scale data streaming, improving analytics in industries like healthcare, gaming, and finance.
- Cloud-Native Solutions: Scalable cloud platforms will make stream processing more accessible, enabling businesses of all sizes to harness real-time analytics.
- Industry-Specific Applications: Real-time analytics will drive innovation in personalized healthcare, dynamic supply chains, smart cities, and financial fraud detection.
- Security and Compliance: Future frameworks will focus on securing streaming data and ensuring compliance with evolving privacy regulations.
- Smarter Automation: Integration with robotics and automation systems will enable faster, data-driven decision-making across industries.
The future of data streams is real-time, efficient, and highly intelligent, reshaping how businesses operate and innovate.
Conclusion
Data streams are the backbone of real-time analytics, empowering businesses to stay ahead in a fast-paced world. By leveraging the right tools and strategies, organizations can unlock the full potential of streaming data, transforming challenges into opportunities. For any organization aiming to thrive in the era of big data, integrating data streams into their analytics framework is not just an option—it’s a necessity.
| For AR-VR Notes | Click Here |
| For Big Data Analytics (BDA) Notes | Click Here |
FAQ’s
What are data streams in analytics?
Data streams are continuous flows of real-time data from sources like IoT devices, social media, and financial systems, used for immediate processing and analysis.
Why are data streams important?
They enable real-time decision-making, improve operational efficiency, and provide up-to-date insights critical for industries like healthcare, finance, and retail.
What tools are used for data stream processing?
Popular tools include Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, Amazon Kinesis, and Google Cloud Pub/Sub.
Which industries benefit the most from data streams?
Industries like IoT, financial services, healthcare, e-commerce, and logistics heavily rely on data streams for real-time analytics.
What challenges do data streams pose?
Key challenges include high infrastructure demands, ensuring data quality, minimizing latency, and maintaining security.