Ethereum and its Components: An Introduction
Introduction of Ethereum and its Components 2025 – Ethereum is more than just a cryptocurrency; it’s a decentralized platform that allows developers to build and deploy smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Since its creation in 2015 by Vitalik Buterin, Ethereum has grown to be one of the most widely-used blockchain networks.

Unlike Bitcoin, which is primarily a digital currency, Ethereum provides a broader ecosystem for decentralized applications, making it an exciting innovation in the world of blockchain.
Key Components of Ethereum
- Ethereum Blockchain: Just like Bitcoin, Ethereum runs on a blockchain, a public distributed ledger where all transactions are recorded. However, the Ethereum blockchain does more than store transactions—it also stores smart contracts and DApps.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The EVM is the core component that allows smart contracts to run on the Ethereum network. It is a decentralized computation engine that ensures smart contracts execute as programmed. It’s what makes Ethereum a “world computer,” allowing the deployment of decentralized apps (DApps) and smart contracts globally.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. They automatically execute when conditions are met, cutting out the need for intermediaries, which saves time and reduces costs.
- Ether (ETH): Ether is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. It’s used to pay for transaction fees and computational services on the network. Ether is also used as “gas” to power smart contracts and run applications.
- Accounts in Ethereum: There are two types of accounts in Ethereum: Externally Owned Accounts (EOA) and Contract Accounts. EOAs are controlled by private keys, while contract accounts are controlled by their associated smart contract code.
- Ethereum Mining: Mining in Ethereum involves solving complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Miners use their computational power to solve these problems, earning rewards in Ether. Ethereum’s consensus mechanism has transitioned from Proof of Work (PoW) to Proof of Stake (PoS) with its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, which is designed to make the network more sustainable and secure.
Architecture and Workflow of Ethereum
The Ethereum network is composed of nodes, which maintain the entire Ethereum blockchain. These nodes communicate with each other to validate transactions, store blockchain data, and execute smart contracts. Ethereum’s architecture consists of four main layers:
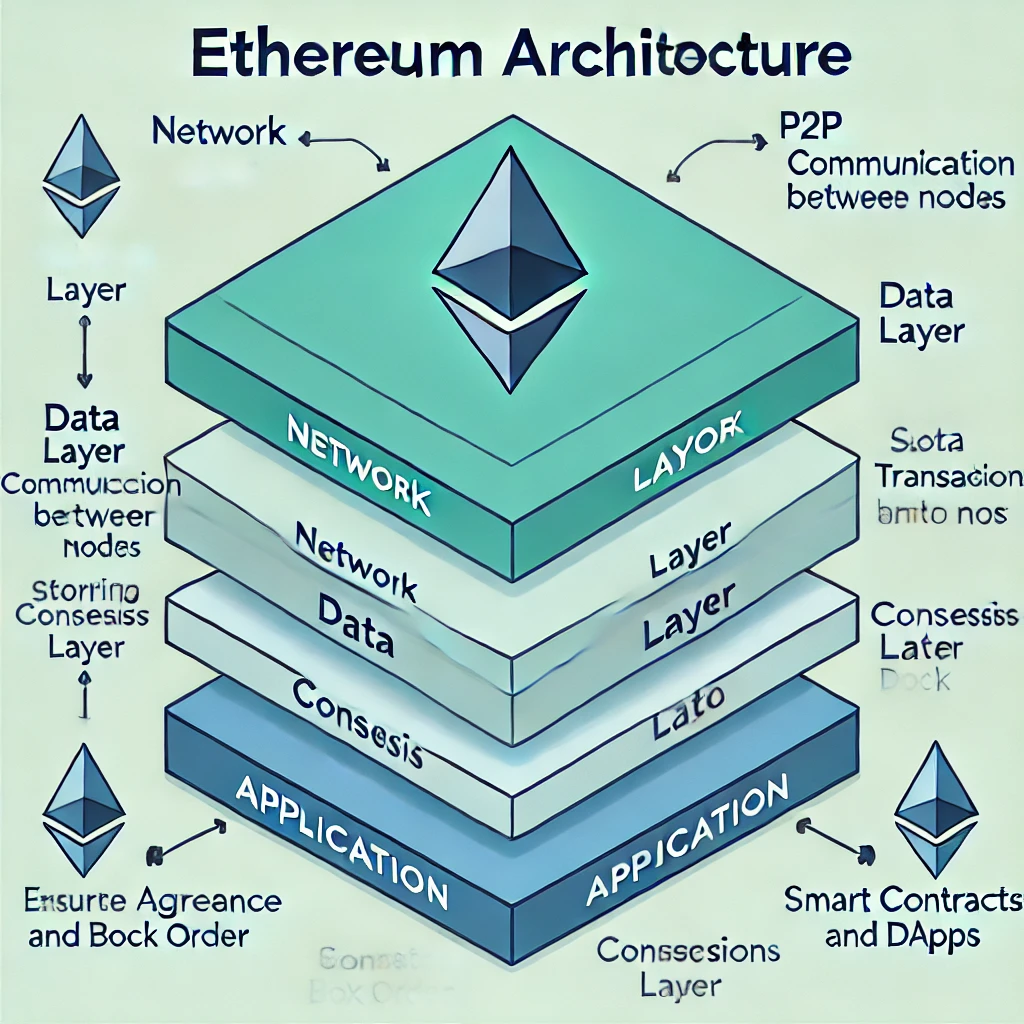
- Network Layer – Nodes communicate with each other through the P2P network.
- Data Layer – This layer stores all the transactions and states of the Ethereum blockchain.
- Consensus Layer – It ensures that all nodes in the network agree on the state of the blockchain and helps achieve the correct block order.
- Application Layer – This is where the smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) live.
When you send a transaction or deploy a contract on Ethereum, your action is broadcast to the network. Ethereum miners (or validators in PoS) then process the transaction, verify it, and add it to the blockchain.
Comparison Between Bitcoin and Ethereum
| Feature | Bitcoin | Ethereum |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Digital currency (store of value) | Smart contracts & DApps |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| Transaction Speed | 10 minutes per block | 12-15 seconds per block |
| Block Time | ~10 minutes | ~12-15 seconds |
| Supply Cap | 21 million coins | No fixed supply cap |
| Issuance Rate | Halved every 4 years (Bitcoin halving) | Variable, with deflationary mechanisms (EIP-1559) |
| Smart Contracts | Limited scripting, not programmable | Full support for smart contracts |
| Transaction Fees | Based on block size and demand | Based on gas (computational cost of operations) |
| Scalability | Low (high fees, slower transactions) | Higher scalability with Ethereum 2.0 upgrade |
| Energy Consumption | High (due to PoW) | Low (due to PoS in Ethereum 2.0) |
| Development Focus | Stability, security | Flexibility, DApps, DeFi |
| Governance Model | Conservative (BIPs) | Active and dynamic (EIPs) |
| Community | Large, conservative | Large, active, and experimental |
| Main Use Case | Store of value, peer-to-peer currency | Decentralized applications, smart contracts, DeFi, NFTs |
| Transaction Finality | Long finality (confirmation needed) | Faster finality with PoS (under Ethereum 2.0) |

Advantages of Ethereum
- Smart Contract Support: Ethereum’s ability to create and execute smart contracts is a huge advantage over Bitcoin. It opens doors to decentralized applications (DApps), making the network much more versatile.
- Faster Transactions: Ethereum’s block time is significantly shorter than Bitcoin’s, making transactions faster and more efficient.
- Decentralization and Security: Ethereum maintains its decentralization while constantly evolving to improve security, especially with the transition to Proof of Stake.
- Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade: The upgrade to PoS will reduce energy consumption and offer a more scalable solution, allowing more transactions per second (TPS).
Disadvantages of Ethereum
- Scalability Issues: While Ethereum is evolving, it still faces issues with scalability. The network can become congested when there are too many transactions.
- High Gas Fees: In periods of high demand, Ethereum gas fees can spike, making transactions costly.
- Complexity for New Users: Ethereum’s technical components, like smart contracts and DApps, can be difficult for newcomers to understand and use.
Introduction of Ethereum and its Components 2025 -FAQs
What is the difference between Bitcoin and Ethereum?
Bitcoin is a digital currency, while Ethereum is a platform for building decentralized applications and running smart contracts. Ethereum has more use cases, such as DApps, while Bitcoin is primarily for value storage and transfer.
What is the role of Ether in Ethereum?
Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. It is used for transaction fees and as “gas” to execute smart contracts and run decentralized applications.
How does Ethereum mining work?
Ethereum mining involves solving computational puzzles to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Miners are rewarded with Ether. Ethereum is transitioning to a Proof of Stake mechanism, which will replace mining with validators.
Summary
Ethereum is a powerful blockchain platform that goes beyond the basic functions of cryptocurrency. It enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications, making it an important player in the world of blockchain technology. With its ongoing upgrades and improvements, particularly with Ethereum 2.0, it promises to be even more scalable and sustainable. However, like all technology, it has its limitations, such as scalability issues and high transaction fees during peak times. As it continues to evolve, Ethereum is set to revolutionize industries by offering a decentralized and transparent platform for innovation.
What Are Avalanches 3 Blockchains?
Comparison Between Bitcoin and Ethereum 2025
Hey everyone! If you have any questions or thoughts, feel free to drop a comment. Let’s learn and discuss together. Your feedback is always welcome!
Hey everyone! If you have any questions or thoughts, feel free to drop a comment. Let’s learn and discuss together. Your feedback is always welcome!

