Marker Detection in Augmented Reality: How It Works and Why It Matters
Augmented Reality (AR) has transformed the way we interact with digital content by blending virtual elements into the real world. One of the core technologies that make AR possible is marker detection. This method allows AR applications to recognize specific objects or patterns and overlay digital information onto them. Marker detection plays a crucial role in various fields, from gaming and education to medical and industrial applications.

Marker Detection in Augmented Reality 2025
What is Marker Detection?
Marker detection is a computer vision technique that helps an AR system identify specific images, symbols, or objects in the real world. Once detected, these markers serve as reference points for placing digital content, such as 3D models, animations, or interactive elements.
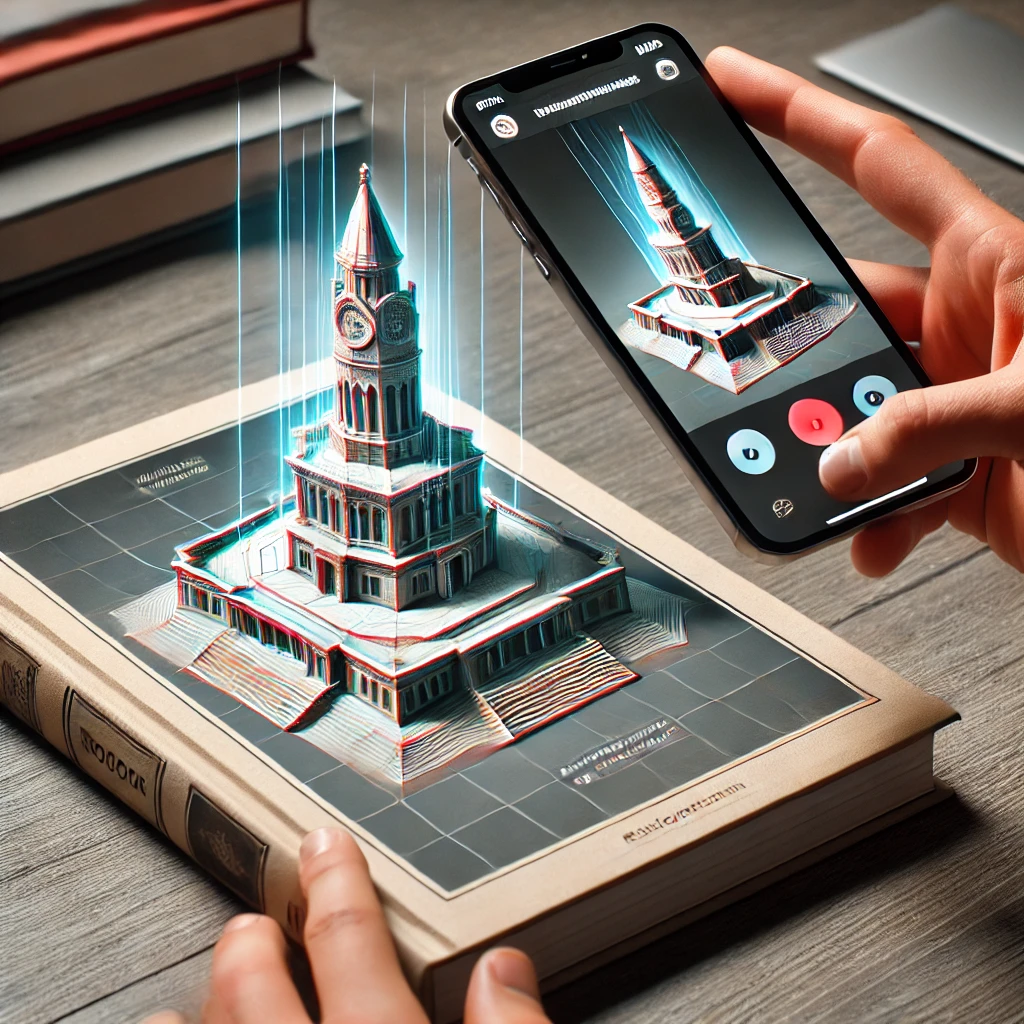
Imagine holding a magazine with a QR code, and when you scan it with your phone, a 3D animation of the product appears on the screen. That is marker detection in action.
How Does Marker Detection Work?
Marker detection involves several steps that allow AR applications to recognize and process a marker efficiently:
1. Capturing the Image
The AR application first captures an image of the surroundings using a camera. This image is then analyzed to find potential markers.
2. Detecting the Marker
The system scans the image for a predefined pattern, symbol, or shape that it recognizes as a marker. These markers can be in the form of QR codes, barcodes, printed images, or even special symbols.
3. Extracting Marker Information
Once a marker is found, the system extracts important details like its position, orientation, and scale. This helps in placing virtual content accurately.
4. Overlaying Virtual Content
After analyzing the marker, the system overlays digital content onto it. For example, in a shopping app, when you point your camera at a clothing catalog, a virtual try-on feature appears.
5. Updating in Real-Time
Marker-based AR updates continuously as you move the camera around. This means the digital objects stay locked onto the real-world marker, even if you tilt, rotate, or move closer.
Types of Markers Used in AR
Different types of markers are used for different AR applications. The most common ones include:
1. QR Codes and Barcodes
These are simple and widely used markers that contain encoded information. When scanned, they can trigger actions such as opening a website, displaying text, or launching an AR experience.

2. Image-Based Markers
These markers are custom-designed images that AR apps recognize and track. For example, a business card with a special logo can be scanned to display a 3D model of a product.

3. 3D Object Markers
Unlike 2D images, some AR applications detect real-world objects such as sculptures, toys, or furniture to overlay relevant digital content.
4. Fiducial Markers
These are black-and-white patterns designed for AR tracking. They are used in robotics, engineering, and industrial settings where precise measurements are needed.
Real-Life Applications of Marker Detection
Marker detection is used in many industries to create interactive and engaging experiences. Let’s look at some real-world applications:
1. Education and Learning
Teachers use marker-based AR to make learning more engaging. Imagine opening a history book and scanning an image of a famous monument. A 3D model of the monument appears, allowing students to explore it from all angles.
2. Retail and Shopping
Many brands now use AR to enhance shopping experiences. Customers can scan product labels to see detailed 3D models, product demonstrations, or even try virtual clothing before purchasing.
3. Healthcare and Medicine
In the medical field, marker detection helps doctors visualize 3D models of organs for better understanding and diagnosis. Medical students can scan textbooks to see animated explanations of human anatomy.
4. Gaming and Entertainment
AR gaming often relies on marker detection. Games like Pokémon GO use real-world markers to place virtual characters on the screen. Board games also use interactive AR markers to enhance gameplay.
5. Industrial and Manufacturing
Factories use marker-based AR for quality control and training. Workers can scan machinery to view real-time data, maintenance instructions, or troubleshooting guides.
6. Tourism and Museums
Tourist attractions now feature AR markers that provide additional information, audio guides, or historical facts when scanned. Museums use marker detection to bring artifacts to life with animations and detailed explanations.
7. Automotive Industry
Car companies use AR to enhance the buying experience. Customers can scan a car brochure to see 3D models of vehicles, customize colors, and explore features in a virtual showroom.
Advantages of Marker-Based AR
Marker detection brings several benefits to AR applications:
Fast and Accurate Recognition – Markers are easy to detect and provide accurate tracking.
Cost-Effective – Implementing marker-based AR is cheaper than advanced AR systems that require expensive hardware.
Easy to Use – Users only need a smartphone or tablet to access marker-based AR experiences.
Improved Engagement – Interactive content makes education, shopping, and entertainment more engaging and immersive.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, marker-based AR has some limitations:
Limited to Predefined Markers – The system can only recognize markers that are already programmed.
Lighting Conditions Matter – Poor lighting or reflections can affect marker detection accuracy.
Not Fully Immersive – Unlike markerless AR (which detects the environment freely), marker-based AR requires a printed or physical marker to function.
Future of Marker-Based AR
The future of AR marker detection is promising. As AI and machine learning improve, AR systems will become smarter and more adaptive. Some future possibilities include:
More Advanced Image Recognition – AR will detect more complex patterns and even handwritten notes.
Better Real-World Integration – AR will blend digital content with natural objects without needing printed markers.
Wider Use in Daily Life – Expect to see AR menus in restaurants, AR user manuals for appliances, and even AR-enhanced newspapers!
Marker Detection in Augmented Reality 2025
Marker detection is an essential part of augmented reality, making it possible to place digital objects onto real-world surfaces accurately. It is widely used in education, retail, healthcare, gaming, and more, improving the way we interact with technology.
With rapid advancements in AI and AR technologies, marker-based experiences will become even more interactive, engaging, and accessible to everyone. Whether it’s trying on clothes virtually, learning about historical places, or playing immersive games, marker detection is shaping the future of digital interaction.
Marker Detection in Augmented Reality 2025 – FAQs
1. What is the difference between marker-based and markerless AR?
Marker-based AR requires a physical marker to trigger AR content, while markerless AR detects real-world surfaces without predefined markers.
2. Can any image be used as an AR marker?
Not all images work as markers. The image should have distinct patterns and high contrast for accurate recognition.
3. Do I need an AR headset for marker detection?
No, most marker-based AR applications work on smartphones and tablets with a camera and AR-supported app.
Marker Detection in Augmented Reality 2025
| For AR-VR Notes | Click Here |
| For Big Data Analytics (BDA) Notes | Click Here |

