Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025 : Imagine you’re in a virtual world, like a video game or virtual reality (VR), exploring a 3D space. To move and interact in this world, you need to understand two key concepts: position and orientation. These terms define where you are and which way you’re facing in the virtual environment.

Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025
What is Position in Virtual Worlds?
Position: This is where you are located in the virtual world. In real life, if you walk forward or backward, you change your position in space. Similarly, in VR, you can change your position by physically moving around or using controls like a joystick to move in the virtual space.
Position tells you where you are. Think of it like your location on a map. In virtual worlds, this is often represented by three numbers, called coordinates (X, Y, Z):
- X: How far left or right you are.
- Y: How high or low you are.
- Z: How far forward or backward you are.
For example:
If you’re playing a game, your character might be at position (3, 2, 5). This means:
- 3 steps to the right,
- 2 steps up,
- 5 steps forward.
In real life, it’s like standing in a room. If you take a few steps forward and then to the left, your position changes.
What is Orientation in Virtual Worlds?
Orientation: This is how you are facing in the virtual world. In real life, when you turn your head or body, your orientation changes. The same happens in VR, where turning your head, tilting, or rotating changes how you view the world around you.
Orientation tells you which direction you are facing. Imagine standing in your living room. If you turn to face the door, then turn again to face the window, your position hasn’t changed, but your orientation has.
In virtual worlds, orientation is often described using three angles: pitch, yaw, and roll:
- Pitch: Tilting your head up or down (like nodding “yes”).
- Yaw: Turning your head left or right (like shaking your head “no”).
- Roll: Tilting your head side to side (like tipping your head to touch your shoulder).
Daily Life Example: Driving a Car
Think about driving a car.
- Your position changes as you move along the road.
- Your orientation changes when you steer left or right or go uphill/downhill.
In a VR driving simulator, the game tracks both your position on the road and your orientation to make the experience feel real.
2. Example: Imagine playing a VR game where you’re standing in the middle of a room, and you turn your head to look around. As you do this, your orientation changes. If you start walking in any direction, your position changes in the game too.
Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025 : How Geometry Shapes Virtual Worlds
In virtual worlds, geometry is the foundation for everything. It defines the space, objects, and how they interact. Without geometry, we wouldn’t have realistic movement or accurate visuals. Here are some key concepts:
- Coordinate System:
Virtual worlds use a 3D grid, just like graph paper but with an extra dimension. This helps locate objects and players in the space. - Transformations: These are mathematical operations that change the position, orientation, and size of objects in the virtual world. For example, when you move an object, rotate it, or resize it, you are applying a transformation. (These transformations are key to creating interactive and dynamic virtual environments.)
Transformations are how objects change their position, size, or shape. For example: - Collisions and Boundaries:
Geometry also ensures you don’t walk through walls or fall through the floor in VR. This is called collision detection.
Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025 Real-Life Analogy:
- Position: Think of yourself walking in a room. Your position changes based on how far you move in different directions (left, right, forward, backward).
- Orientation: Now, think of how you turn your head or body to face different objects. Your orientation changes based on where you’re looking.
In a virtual world, similar movements happen through your headset or controllers. As you walk or move, the system tracks your position. As you turn your head or hands, the system tracks your orientation.
1.Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025 3D cube in Virtual Space
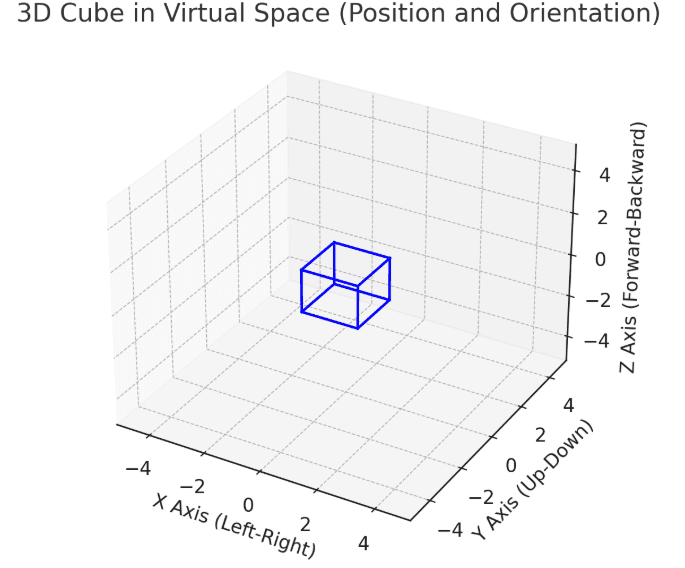
Diagram Explanation: Position and Orientation in a 3D Virtual Space
In the diagram, we have a 3D cube that represents an object in a virtual world. The cube’s position and orientation are defined in a 3D coordinate system, just like how objects are placed and moved in real life.
1. Position:
- X-Axis (Left-Right): The cube can move along the X-axis, shifting left or right. In real life, think of how you move sideways (left or right) while walking.
- Y-Axis (Up-Down): The cube also moves along the Y-axis, which represents vertical movement. In real life, this would be like jumping up or crouching down.
- Z-Axis (Forward-Backward): The cube moves along the Z-axis, which represents depth in space—moving forward or backward. Imagine walking forward towards something or stepping backward.
The position of the cube can be anywhere in this 3D space, depending on where it is placed along these axes. For example, the cube’s center might be at coordinates (0,0,0), and it can move to any position within the defined limits of the space.
2. Orientation:
The orientation of the cube refers to how it rotates or faces different directions within the 3D space.
- X-axis Rotation (Tilt): The cube can tilt forward or backward. This is like how you tilt your head up to look at the sky or down to look at the ground.
- Y-axis Rotation (Turn Left/Right): The cube can rotate left or right around its vertical axis. This is similar to turning your body or head to the left or right to look at something.
- Z-axis Rotation (Twist): The cube can twist around the Z-axis, which would be like rotating your body around the center, making you face different directions.
Real-Life Analogy:
- Position: Think about walking in a room. You can move left-right, up-down (on stairs or lifting your arms), or forward-backward (walking towards a door).
- Orientation: Imagine looking around a room by turning your head. Your body and head turn in different directions, changing your view of the space.
2. Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025 X, Y, and Z axes

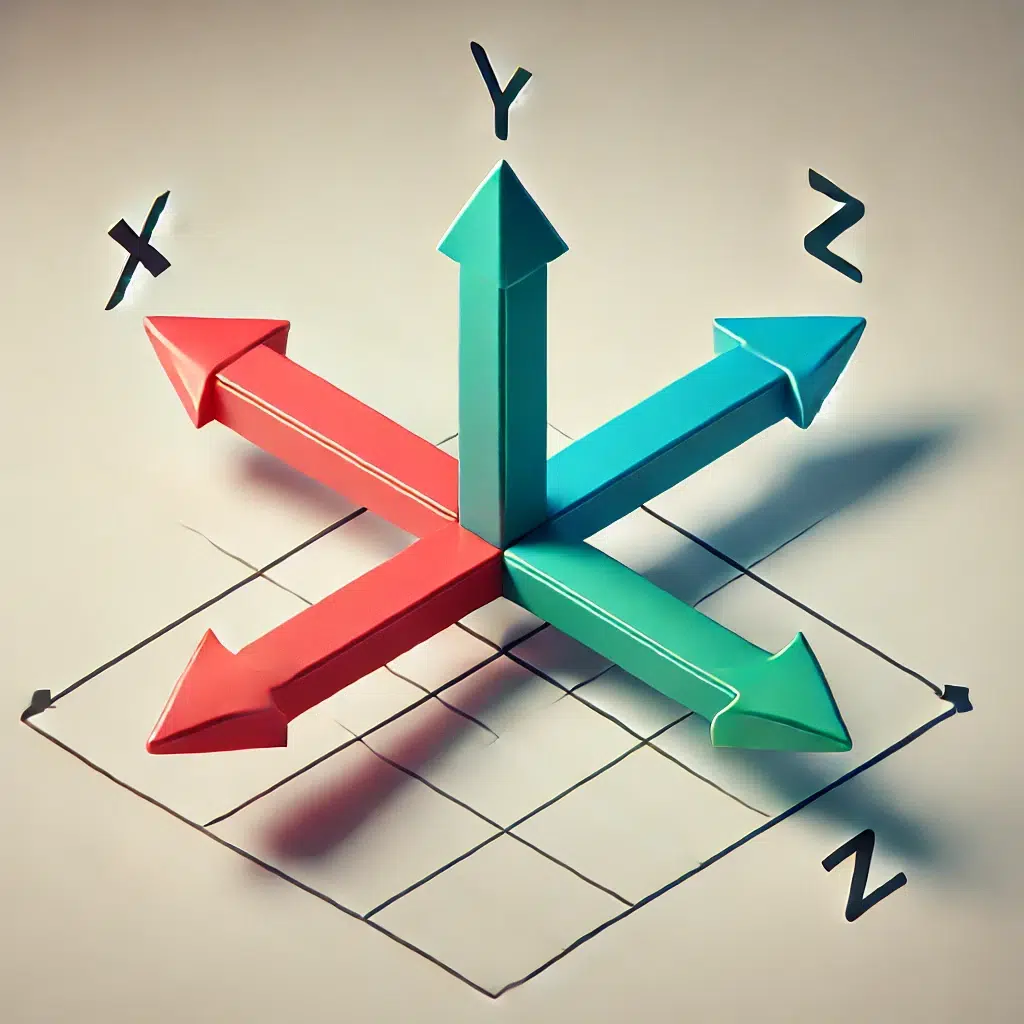
Here’s a simplified explanation and description of the X, Y, and Z axes, along with a diagram.
Explanation of X, Y, and Z Axes
- X-Axis (Horizontal):
- Think of it as a line going left and right.
- Example: Walking sideways in a room.
- Y-Axis (Vertical):
- This line goes up and down.
- Example: Moving an elevator up or down.
- Z-Axis (Depth):
- This line goes in and out, adding a sense of depth.
- Example: Walking forward or backward.
In virtual worlds or 3D spaces, these axes work together to define your position in space. The origin (where X, Y, and Z meet) is like your starting point.
Diagram Description
The diagram has:
- Red arrow for X-axis (left to right).
- Green arrow for Y-axis (up and down).
- Blue arrow for Z-axis (forward and backward).
- All three arrows meet at a single point, called the origin.
- Red arrow (X-axis): Moves left to right.
- Green arrow (Y-axis): Moves up and down.
- Blue arrow (Z-axis): Moves forward and backward (depth).
Real-World Applications of Virtual Geometry
- Gaming:
When you play games like Minecraft, Call of Duty, or VR sports, the position and orientation of your character define your gameplay experience. - VR Workouts:
Apps like Beat Saber track your hand’s position and orientation to match your movements with the rhythm. - AR Navigation:
Augmented Reality (AR) apps, like Google Maps AR, use geometry to show you arrows or directions that match your position in the real world. - Robotics and Drones:
Just like in virtual worlds, drones and robots use position and orientation to navigate physical spaces.
Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025 – Challenges in Virtual Geometry
- Precision:
Small errors in position or orientation can make movements look unrealistic or “glitchy.” - Performance:
Calculating geometry in real time for VR or games requires powerful computers. - User Comfort:
Incorrect orientation in VR can cause motion sickness.
Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025
Understanding position and orientation in virtual worlds makes the experience feel natural and immersive. From gaming to navigation, this geometry connects the virtual and real worlds. It’s amazing how these mathematical concepts create spaces where we can play, learn, and interact.
Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025 FAQs
Q: Why is position important in VR?
A: Position helps track where you are in the virtual world, making movements and interactions realistic.
Q: How does orientation affect VR experiences?
A: Orientation determines the direction you’re facing, helping VR apps adjust visuals and interactions to match your view.
Q: Can virtual geometry be applied in real life?
A: Yes! Drones, robotics, and AR apps all use geometry similar to virtual worlds to navigate and interact with real spaces.
Position and Orientation in Virtual Worlds 2025
| For AR-VR Notes | Click Here |
| For Big Data Analytics (BDA) Notes | Click Here |

