Blockchain in Everyday Life: Uses, Tools, Advantages, and Challenges
Introduction
Tools and Applications of Blockchain 2025 – Blockchain might sound like a complex tech term, but it is something that is slowly becoming a part of our daily lives. From banking to shopping online, blockchain is transforming the way we store and share data.

What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a digital ledger that records transactions securely and transparently. Think of it as a diary that cannot be erased or edited. Every time a new entry (transaction) is made, it gets added to the chain, making it highly secure and nearly impossible to hack.
How Blockchain Works (With Examples)
- Transaction Happens – Suppose Alice wants to send money to Bob using cryptocurrency. She initiates a transaction.
- Verification – The transaction is verified by multiple computers (nodes) in the blockchain network to ensure authenticity.
- Block Creation – Once verified, Alice’s transaction is grouped with other transactions to form a new block.
- Added to Blockchain – The block is added to the chain, making it a permanent and secure record.
Tools and Applications of Blockchain 2025
Applications of Blockchain (With Examples)
Blockchain is used in various sectors, making our lives easier and more secure. Here are some common applications:
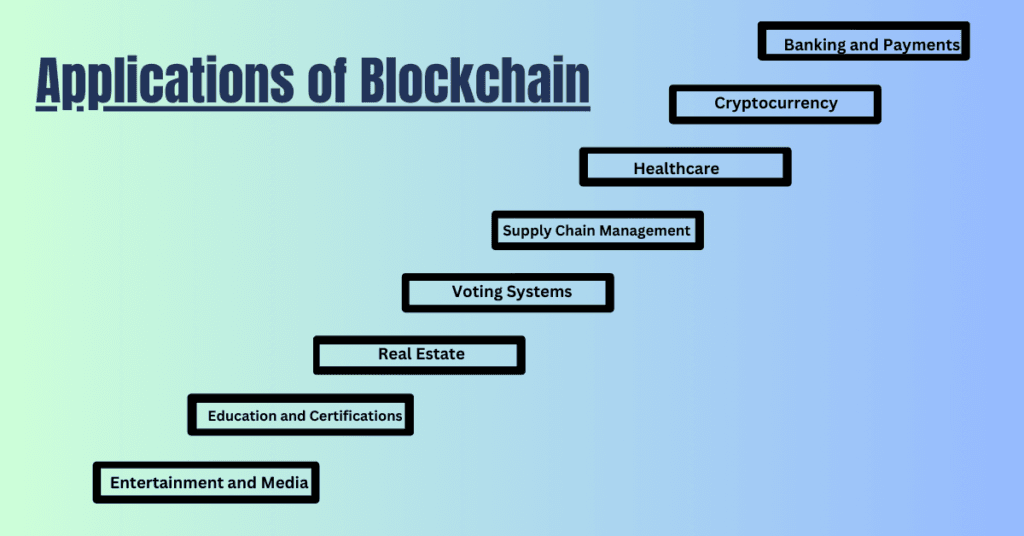
1. Banking and Payments
- Example: If John wants to send money overseas using traditional banking, it may take days. With blockchain-based payments like Bitcoin or Ripple, the transaction can be completed within minutes and at lower costs.
- Blockchain also helps in reducing fraud as every transaction is transparent and cannot be altered.
2. Cryptocurrency
- Example: Bitcoin and Ethereum are popular digital currencies that use blockchain to store transaction records securely, preventing fraud and double-spending.
- Many businesses now accept cryptocurrency as a form of payment, making transactions seamless and decentralized.
3. Healthcare
- Example: A hospital using blockchain can store patient records securely. If a patient visits a different hospital, doctors can access their records without needing paper files, reducing errors and improving treatment.
- Blockchain helps prevent counterfeit medicines by tracking the supply chain of pharmaceutical products.
4. Supply Chain Management
- Example: A company like Walmart uses blockchain to track food products from farm to store. If a product is found defective, they can trace it back to the exact farm it came from, ensuring food safety.
- Other industries use blockchain to ensure the authenticity of luxury goods like designer handbags and watches.
5. Voting Systems
- Example: Governments can use blockchain-based voting systems to ensure fair elections. Estonia has already implemented blockchain in its voting system, making elections more transparent and secure.
- Blockchain prevents voter fraud by ensuring that each vote is recorded and cannot be altered or duplicated.
6. Real Estate
- Example: Buying property often involves paperwork and middlemen. Blockchain can store property ownership details securely, eliminating fraud and speeding up transactions.
- With smart contracts, transactions can be automated, reducing the need for manual verification.
7. Education and Certifications
- Example: Universities and institutions can store certificates and degrees on a blockchain, preventing fake degrees and forgery.
- Employers can verify a candidate’s credentials instantly without needing to contact the university.
8. Entertainment and Media
- Example: Musicians and content creators can use blockchain to protect their copyrights and ensure they get paid fairly for their work.
- Platforms like Audius use blockchain to allow artists to distribute their music directly to fans without intermediaries.
Popular Blockchain Tools (Explained in Depth)
There are various tools and platforms that help developers and businesses use blockchain technology efficiently. Here are some popular ones with detailed explanations:
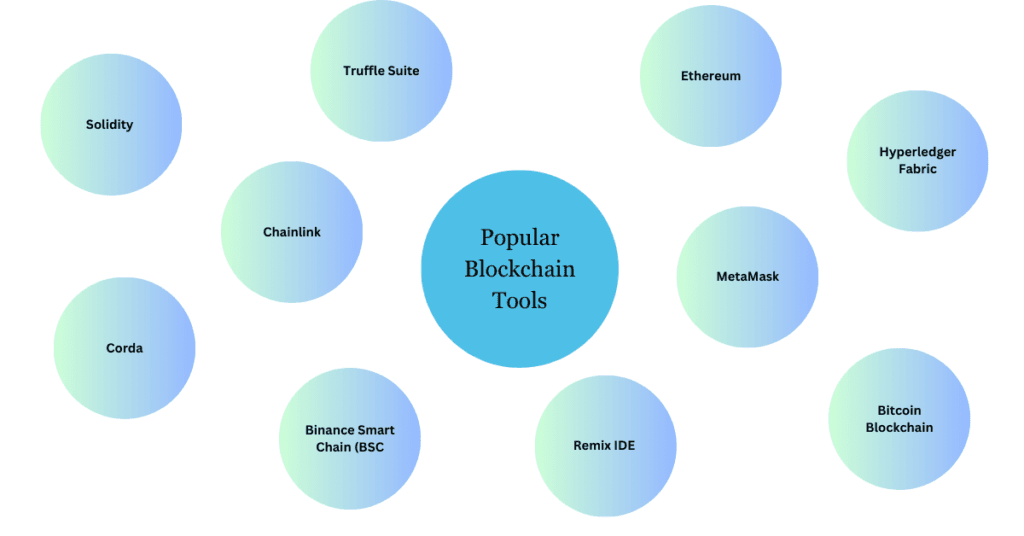
- Ethereum – A decentralized platform that allows developers to create smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps). Ethereum enables automated transactions without intermediaries, making it a favorite for blockchain developers.
- Hyperledger Fabric – A permissioned blockchain framework designed for businesses. Unlike public blockchains like Ethereum and Bitcoin, Hyperledger Fabric allows only authorized participants to access data, making it ideal for enterprise use cases like banking and supply chain management.
- Bitcoin Blockchain – The first and most popular blockchain network, primarily used for Bitcoin transactions. It ensures secure peer-to-peer transactions without the need for a central authority.
- Corda – A blockchain platform designed for businesses, focusing on privacy and efficiency. Unlike traditional blockchains, Corda does not broadcast all transactions to the entire network, making it more scalable and secure for financial applications.
- Solidity – A programming language specifically designed for writing smart contracts on Ethereum. It allows developers to create automated agreements that execute based on predefined rules, removing the need for third-party intervention.
- Truffle Suite – A development framework for Ethereum-based applications. It provides testing, deployment, and management tools, making it easier for developers to build and maintain blockchain applications.
- Remix IDE – A web-based tool used for writing, testing, and deploying Ethereum smart contracts. It is an essential tool for blockchain developers who want to create and debug smart contracts quickly.
- MetaMask – A browser extension and mobile app that enables users to interact with Ethereum-based DApps. It acts as a digital wallet, allowing users to store and manage cryptocurrencies securely.
- Chainlink – A decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts with real-world data. For example, a smart contract in insurance can use Chainlink to access weather data before processing a claim automatically.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC) – A blockchain network designed for fast and low-cost transactions. It is widely used for decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and NFT (non-fungible token) marketplaces.
Advantages of Blockchain
- Highly Secure – Once data is stored, it cannot be changed or hacked easily.
- Transparency – Every transaction is recorded and visible to authorized users.
- Decentralization – No middleman is required, reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Faster Transactions – No waiting time like traditional banking systems.
- Lower Costs – No extra fees for middlemen like banks or brokers.
- Trust and Reliability – Transactions are verified by multiple nodes, ensuring trust among users.
- Automation with Smart Contracts – Contracts execute automatically when conditions are met, reducing delays.
Disadvantages of Blockchain
- High Energy Consumption – Some blockchain networks use a lot of electricity.
- Scalability Issues – Large transactions can slow down the system.
- Regulatory Challenges – Some governments are still figuring out how to regulate blockchain.
- Risk of Losing Private Keys – If a user loses their private key, they lose access to their assets forever.
- Complexity for Beginners – Some users find blockchain technology difficult to understand and use.
- Data Privacy Concerns – Even though blockchain is secure, some public blockchains make transaction details visible to everyone.
FAQs – Tools and Applications of Blockchain 2025
1.Is blockchain only for Bitcoin?
No, blockchain is used in many fields, including healthcare, real estate, and banking.
2. Can blockchain be hacked?
It is extremely difficult to hack because it is decentralized and secured with encryption.
3. Do I need technical knowledge to use blockchain?
Not necessarily. Many user-friendly applications use blockchain without requiring technical knowledge.
4. What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules, ensuring automated and trustless transactions.
5. How is blockchain different from traditional databases?
Traditional databases are centralized, while blockchain is decentralized, making it more secure and transparent.
6. Can blockchain be used for identity verification?
Yes, blockchain can store and verify identities securely, reducing fraud and identity theft.
Tools and Applications of Blockchain 2025 :
3 Key Consensus Algorithms for Private Blockchains
PoB in Bitcoin Blockchain 2025 : A Detailed Guide
Hey everyone! If you have any questions or thoughts, feel free to drop a comment. Let’s learn and discuss together. Your feedback is always welcome!