Understanding Proof-of-Stake (PoS) in Bitcoin Blockchain: A Day-to-Day Guide
Understanding PoS in Bitcoin Blockchain 2025 – Blockchain technology, the backbone of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, has been gaining immense popularity in recent years. While most people are familiar with the basics of Bitcoin, its underlying technology, such as Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS), may seem a bit more complex. In this post, we’ll take a look at PoS, its role in the Bitcoin blockchain, and how it compares to PoW in simple terms, using everyday scenarios to help you understand it better.

What is Proof-of-Stake (PoS)?
To start, let’s break down the concept of Proof-of-Stake. Imagine you are part of a community where members need to decide whether or not a new rule should be adopted. In traditional decision-making, you might vote based on your opinion. In the case of PoS, your “vote” is based on how much of the cryptocurrency (Bitcoin, for example) you own or “stake.”
PoS is a consensus algorithm that allows people to verify transactions and add new blocks to a blockchain, but instead of using energy-consuming puzzles (as seen in Proof-of-Work), it uses the principle of staking cryptocurrency. The more cryptocurrency you have staked, the more likely you are to be chosen as a validator, which means you can propose new blocks and validate transactions.

PoS in the Bitcoin Blockchain
Now, you might wonder, if PoS is so efficient, why doesn’t Bitcoin use it? Well, Bitcoin primarily relies on Proof-of-Work, where miners use computational power to solve complex puzzles to validate transactions. However, the idea of PoS in Bitcoin has been gaining traction. Let’s explore how PoS would work in the Bitcoin blockchain.
In a PoS-based Bitcoin blockchain, users would be required to lock up a certain amount of Bitcoin to participate in the network as validators. Validators would be chosen randomly, but the chances of being selected would depend on how much Bitcoin a user has staked. This means that if you hold a large amount of Bitcoin, your chances of validating transactions and earning rewards are higher. If you act maliciously, your staked Bitcoin could be forfeited, making it a secure system.
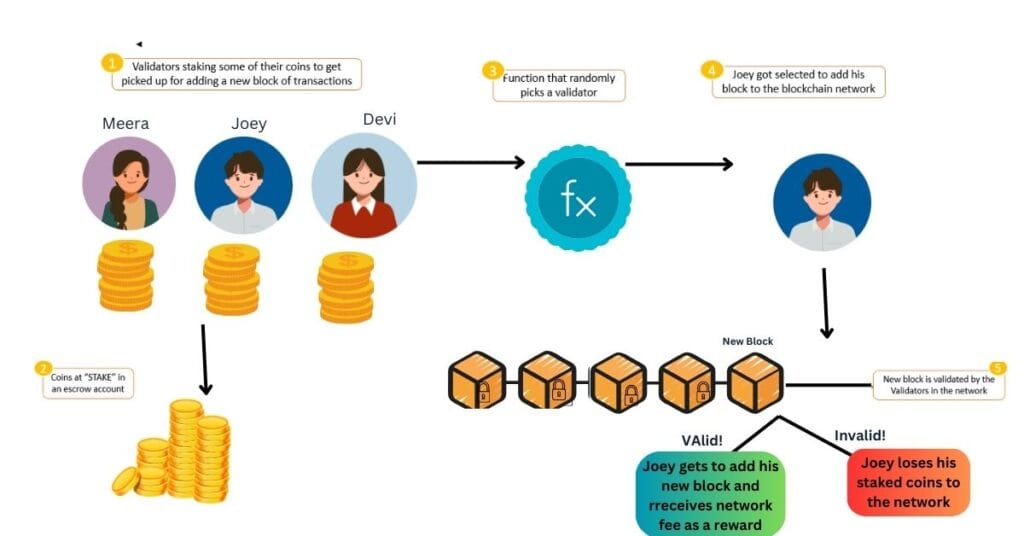
How Does Proof-of-Stake Affect Day-to-Day Life?
Understanding PoS might seem complicated at first, but let’s try to relate it to day-to-day scenarios.
1. Saving Money in a Bank:
Imagine you’re putting your money in a bank. In a PoS system, this is like depositing your funds in a savings account where you receive interest. The more money you have in your account (the more Bitcoin you stake), the higher your chances of being rewarded with additional Bitcoin. You can think of these rewards as interest on your savings.
2. Voting in a Community Election:
PoS is like voting in a community election, but with a twist. Instead of each person getting one vote, the more Bitcoin you stake, the more “voting power” you have. In a sense, your stake determines your influence over the network’s decisions, making you a “stakeholder” in the network’s governance.
3. Risk of Losing Your Staked Bitcoin:
Think about staking your Bitcoin as locking it up in a safe deposit box. If you behave dishonestly (e.g., trying to cheat the system), you could lose the keys to your box, meaning you’d lose your Bitcoin. This ensures that everyone in the system acts honestly to maintain the integrity of the network.
Advantages of Proof-of-Stake
1. Energy Efficiency
One of the major benefits of PoS is its low energy consumption. In PoW, miners use powerful computers to solve complex mathematical problems, consuming vast amounts of energy. On the other hand, PoS doesn’t require the same energy-heavy processes, making it a much more environmentally friendly option.
For example, imagine you are baking a cake in an oven. If you use a small oven (PoS), it consumes less energy, but if you use a huge industrial oven (PoW), you’ll need far more energy to bake the same cake. PoS is the small oven in this analogy.
2. Cost-Effective
PoS also reduces the cost of participation. In PoW, miners need to invest in expensive hardware and electricity. With PoS, you only need to “stake” your cryptocurrency, eliminating the need for costly equipment. This makes it more accessible to people who may not have the resources to mine Bitcoin but want to participate in the network.
3. Greater Security
Since PoS relies on staked cryptocurrency, it becomes very costly for malicious actors to attack the network. For example, in PoS, if someone tries to attack the system, they risk losing their staked Bitcoin. The risk of losing money acts as a deterrent, creating a more secure environment for transactions.
4. Faster Transaction Processing
With PoS, transactions can be processed faster. In PoW, the time it takes to solve complex puzzles and confirm a block can be lengthy. In PoS, the process of selecting validators and confirming blocks is quicker, leading to faster transaction times.
Disadvantages of Proof-of-Stake
1. Centralization Risks
One of the criticisms of PoS is that it can lead to centralization. If a small group of people own the majority of the Bitcoin in the network, they would have more control over the network’s decisions. This could make the system less democratic and decentralized, which is one of the key ideals behind cryptocurrency.
Imagine a voting system where only the wealthiest individuals get to decide the rules. In this case, PoS could be seen as unfair because those with more resources have greater influence.
2. Wealth Concentration
Since PoS rewards users based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake, it could encourage the wealthy to accumulate more Bitcoin. This could result in a situation where the rich get richer, potentially creating inequality within the network.
3. Security Concerns in Early Stages
While PoS is considered secure, new PoS networks might face some risks in their early stages. Since validators are randomly chosen, there may be vulnerabilities until the network matures and becomes more robust.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Vs. Proof-of-Stork (PoSt)
| Feature | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Proof-of-Stork (PoSt) |
|---|---|---|
| What it is | A system where people who own more cryptocurrency get a chance to validate transactions. | A new idea where people are chosen to validate transactions based on how much data they store. |
| How Validation Works | Validators are picked based on the amount of cryptocurrency they “lock” as a promise to act fairly. | Validators are chosen based on the amount of data they are willing to store for the network. |
| Security | It’s secure because the validators risk losing their staked cryptocurrency if they misbehave. | It’s secure based on the amount of data stored and the validator’s honesty in keeping it safe. |
| Energy Usage | PoS uses much less energy than systems like Proof-of-Work (PoW) since it doesn’t require solving complex puzzles. | PoSt uses even less energy, as it’s more about storage than computation. |
| Scalability | PoS can handle a lot of transactions easily since it doesn’t need heavy calculations. | PoSt can also scale well, as it focuses on storing data rather than performing complex tasks. |
| Rewards | Validators get rewards like transaction fees or new coins for helping keep the network safe. | Validators are rewarded for storing data and keeping it accessible to others. |
| Examples | Used by networks like Ethereum 2.0, Cardano, and Polkadot. | Still a new idea with no major networks using it yet. |
| Main Idea | It rewards people for holding and locking up coins to help maintain the network. | It rewards people for contributing storage space to keep the network running. |
The main difference is that PoS uses staking coins as a way to choose who validates transactions, while PoSt would rely on who stores data in the network.

Understanding PoS in Bitcoin Blockchain 2025 – FAQ
1. How does staking work in Proof-of-Stake?
Staking in PoS means locking up a certain amount of cryptocurrency to participate in the network’s validation process. The more cryptocurrency you stake, the higher your chances of being chosen as a validator.
2. Can I lose my staked Bitcoin?
Yes, if you act maliciously or fail to follow the rules, you could lose your staked Bitcoin. This is a safeguard to maintain the security and integrity of the network.
3. Is Proof-of-Stake better than Proof-of-Work?
PoS offers several advantages, such as lower energy consumption and faster transaction speeds, making it more environmentally friendly and cost-effective. However, PoW remains a tried-and-true system with its own strengths, especially in terms of security.
4. Can Bitcoin switch to Proof-of-Stake?
While Bitcoin currently uses Proof-of-Work, there are ongoing discussions about the potential benefits of switching to PoS. However, this would require significant changes to the Bitcoin protocol, and it’s not clear when or if this will happen.
5. How can I start staking my Bitcoin?
To start staking, you need to find a platform or network that supports PoS. Once you’ve chosen a platform, you’ll need to lock up your Bitcoin in a staking wallet, which will allow you to participate in the network and earn rewards.
Summary
we explored the concept of Proof-of-Stake (PoS), particularly its potential application in the Bitcoin blockchain. PoS offers a more energy-efficient, cost-effective, and secure alternative to Proof-of-Work (PoW), making it an appealing option for the future of cryptocurrency networks. However, it also comes with some challenges, such as centralization risks and the potential for wealth concentration. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of PoS can help you make more informed decisions about participating in blockchain networks, whether you’re a miner, investor, or user.
By comparing PoS with everyday life scenarios, we’ve made this complex concept more accessible and easier to grasp. If you’re interested in learning more or have any questions, feel free to check out our FAQ section.
What is Proof-of-Elapsed Time (PoET)?
The Life of a Bitcoin Miner in 2025 : Understanding Mining Difficulty and Mining Pools

