What Are Avalanche’s Three Blockchains?
What Are Avalanches 3 Blockchains? – Avalanche is one of the fastest-growing blockchain platforms in the world, known for its high speed, security, and scalability. Unlike many other blockchains that operate on a single chain, Avalanche uses a unique approach by integrating three different blockchains within its ecosystem. These blockchains work together to provide a seamless and efficient user experience.
What Is Avalanche?
Avalanche is a decentralized smart contract platform developed by Ava Labs. It is designed to provide high transaction speeds, low fees, and interoperability between different blockchain networks. Avalanche’s main goal is to solve the scalability issues faced by traditional blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum while maintaining decentralization and security.
Unlike other blockchains, Avalanche operates on a unique multi-chain structure that consists of three primary blockchains, each serving a specific purpose. This design allows Avalanche to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS) while maintaining security and decentralization.
The Three Blockchains of Avalanche
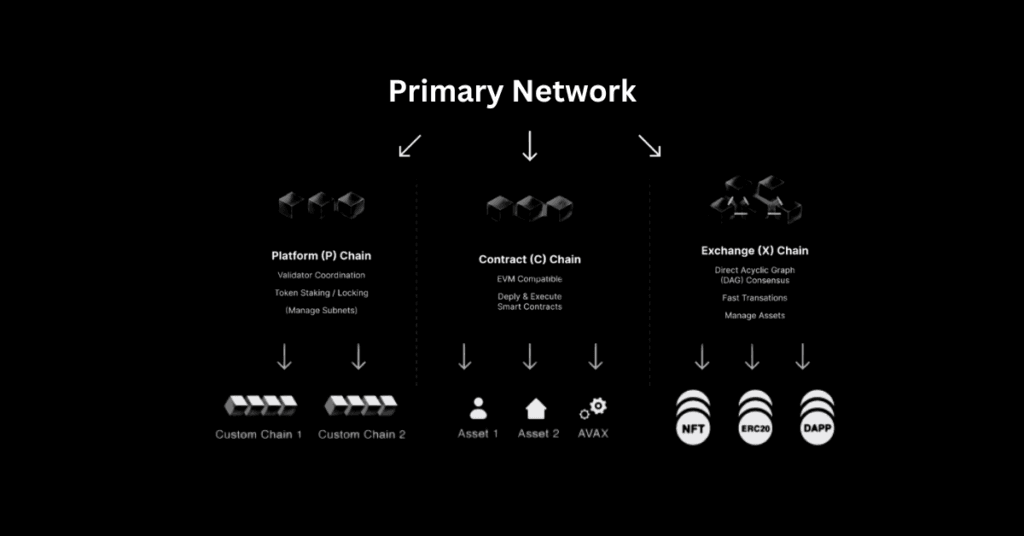
Avalanche is made up of three interconnected blockchains:
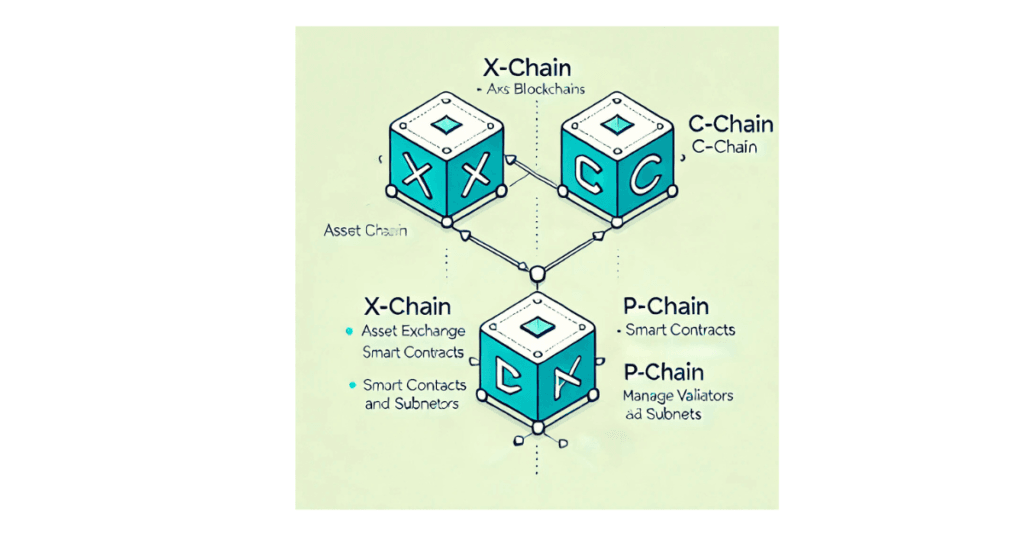
Avalanche uses these three blockchains to work faster and handle different tasks separately.
1. X-Chain (Exchange Chain)
The X-Chain is responsible for handling asset creation and transfers. It is used to send and receive Avalanche’s native token (AVAX) and other custom assets that are built on the platform. The X-Chain operates using a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) consensus mechanism, which allows high-speed and parallel transactions.
How X-Chain Works:
- Uses a DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) structure, enabling parallel transaction processing.
- Transactions do not require global consensus, allowing instant finality.
- Primarily designed for AVAX transactions and custom asset creation.
- Transactions on the X-Chain incur fees paid in AVAX.
Key Features of X-Chain:
- Mainly used for sending and receiving AVAX tokens.
- Uses the Avalanche Consensus Protocol for fast transactions.
- Supports the creation of custom digital assets and tokens.
- Works similarly to a traditional payment system.
Use Cases of X-Chain:
- Transferring AVAX and other digital assets.
- Creating new tokens on the Avalanche network.
- Fast and low-cost peer-to-peer transactions.
2. C-Chain (Contract Chain)
The C-Chain is the blockchain where smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps) are deployed. It is Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible, meaning developers can easily build and migrate Ethereum-based applications to Avalanche.
How C-Chain Works:
- Runs a modified version of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
- Uses the Snowman Consensus Protocol, which is optimized for smart contracts.
- Developers can deploy and interact with Ethereum-compatible smart contracts.
- Allows for DeFi applications, NFT marketplaces, and DAOs to run efficiently.
Key Features of C-Chain:
- Supports smart contracts and dApp development.
- Compatible with Ethereum tools like MetaMask and Remix.
- Uses the Snowman Consensus Protocol, ensuring high security and efficiency.
- Provides low transaction fees compared to Ethereum.
Use Cases of C-Chain:
- Running decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
- Deploying smart contracts.
- Building NFT marketplaces.
- Migrating Ethereum-based projects to a faster, cheaper blockchain.
3. P-Chain (Platform Chain)
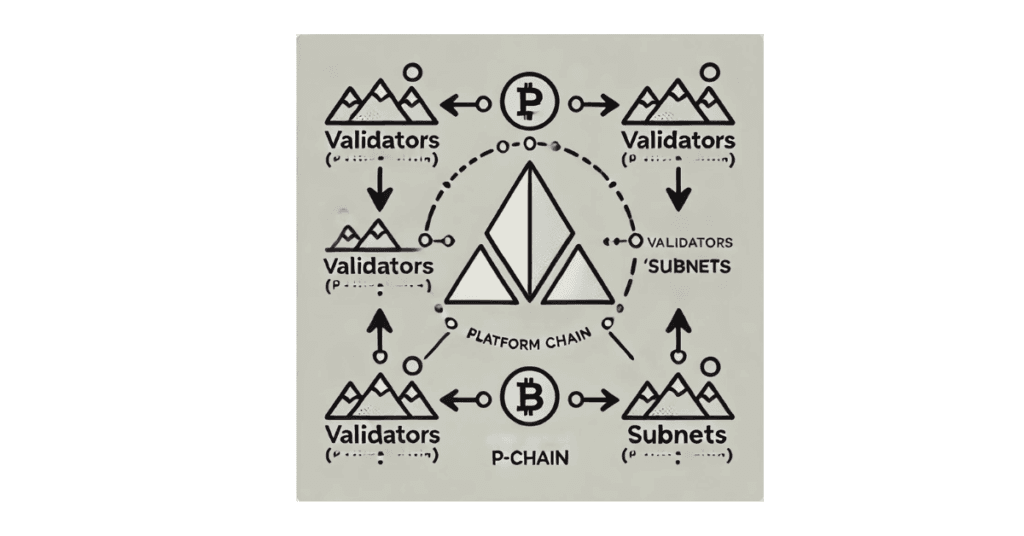
The P-Chain is the administrative and governance chain of Avalanche. It is used for coordinating validators, creating subnets, and managing the overall network structure.
How P-Chain Works:
- Uses the Snowman Consensus Protocol, ensuring strong security.
- Responsible for tracking and coordinating validators.
- Enables the creation of subnets, which are independent blockchains operating on Avalanche.
- Manages AVAX staking and validator rewards.
Key Features of P-Chain:
- Manages validators who secure the Avalanche network.
- Allows the creation of custom subnets (independent blockchains running on Avalanche).
- Uses the Snowman Consensus Protocol for security and efficiency.
- Controls staking of AVAX tokens.
Use Cases of P-Chain:
- Setting up custom blockchains (subnets) for enterprises and developers.
- Staking AVAX to become a network validator.
- Managing network governance and decision-making.
Advantages of Avalanche’s Three-Blockchain Structure
1. High Scalability
- Avalanche can handle thousands of transactions per second due to its multi-chain architecture.
2. Low Transaction Fees
- Unlike Ethereum, Avalanche offers cheaper gas fees, making it more accessible for users and developers.
3. Faster Transactions
- The use of the Avalanche Consensus Protocol allows near-instant transaction finality.
4. Interoperability with Ethereum
- The C-Chain enables developers to migrate Ethereum projects without major changes.
5. Customization through Subnets
- Developers can create independent blockchains tailored to specific use cases.
Disadvantages of Avalanche’s Three-Blockchain Structure
1. Complexity for Beginners
- Understanding and using multiple blockchains may be confusing for new users.
2. Network Congestion Risk
- As more projects launch on Avalanche, congestion could slow down performance.
3. High Competition in the Blockchain Industry
- Avalanche competes with established blockchains like Ethereum, Solana, and Polkadot.
4. Security Concerns for New Subnets
- Subnets may have different security levels, posing risks to certain applications.
What Are Avalanches 3 Blockchains? FAQs
1. Why does Avalanche have three blockchains?
Avalanche has three blockchains to improve efficiency, scalability, and security by separating transactions, smart contracts, and network governance.
2. What is the difference between X-Chain, C-Chain, and P-Chain?
X-Chain is used for sending AVAX and creating assets.
C-Chain is used for smart contracts and dApps.
P-Chain is used for network management and validator coordination.
3. Can I use Avalanche to create my own blockchain?
Yes, Avalanche allows developers to create custom subnets using the P-Chain.
4. How fast are Avalanche transactions?
Avalanche transactions are almost instant and take less than 2 seconds to finalize.
5. Is Avalanche better than Ethereum?
Avalanche offers faster transactions and lower fees than Ethereum, but Ethereum has a larger developer community and ecosystem.
6. Can I transfer Ethereum assets to Avalanche?
Yes, you can use the Avalanche Bridge to move Ethereum-based assets to the Avalanche C-Chain.
Summary
Avalanche’s unique three-blockchain structure makes it one of the most advanced and scalable blockchain platforms available today. Each chain serves a specific purpose: X-Chain for asset transfers, C-Chain for smart contracts, and P-Chain for network management. This structure allows Avalanche to offer fast, secure, and cost-effective blockchain solutions.
By integrating high-speed transactions, low fees, and Ethereum compatibility, Avalanche is becoming a preferred choice for developers and businesses in the blockchain space. Whether you’re a user, developer, or investor, understanding Avalanche’s three-blockchain model can help you make the most of this innovative platform.
Understanding Public Blockchain and Ethereum 2025
How to Use Blockchain Domains 2025
Understanding Private Blockchain 2025
Hey everyone! If you have any questions or thoughts, feel free to drop a comment. Let’s learn and discuss together. Your feedback is always welcome!